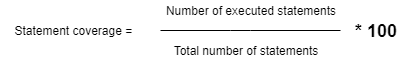Gibt die äußersten Knoten jeder Ebene des Binärbaums in alternativer Reihenfolge aus
 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; } Bei einem gegebenen Binärbaum werden die Knoten der äußersten Ecken jeder Ebene gedruckt, jedoch in anderer Reihenfolge.
Beispiel:

For above tree the output can be 1 2 7 8 31 - print rightmost node of 1st level - print leftmost node of 2nd level - print rightmost node of 3rd level - print leftmost node of 4th level - print rightmost node of 5th level OR 1 3 4 15 16 - print leftmost node of 1st level - print rightmost node of 2nd level - print leftmost node of 3rd level - print rightmost node of 4th level - print leftmost node of 5th levelRecommended Practice Extremknoten in alternativer Reihenfolge Probieren Sie es aus!
Die Idee besteht darin, den Baum Ebene für Ebene zu durchlaufen. Für jede Ebene zählen wir die Anzahl der darin enthaltenen Knoten und geben den Knoten ganz links oder ganz rechts basierend auf dem Wert eines booleschen Flags aus. Wir entfernen alle Knoten der aktuellen Ebene aus der Warteschlange und reihen alle Knoten der nächsten Ebene in die Warteschlange ein und invertieren den Wert des booleschen Flags, wenn wir die Ebene wechseln.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung der obigen Idee:
C++ /* C++ program to print nodes of extreme corners of each level in alternate order */ #include using namespace std ; /* A binary tree node has data pointer to left child and a pointer to right child */ struct Node { int data ; Node * left * right ; }; /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given data and NULL left and right pointers. */ Node * newNode ( int data ) { Node * node = new Node ; node -> data = data ; node -> right = node -> left = NULL ; return node ; } /* Function to print nodes of extreme corners of each level in alternate order */ void printExtremeNodes ( Node * root ) { if ( root == NULL ) return ; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root queue < Node *> q ; q . push ( root ); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed bool flag = false ; while ( ! q . empty ()) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q . size (); int n = nodeCount ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( n -- ) { Node * curr = q . front (); // Enqueue left child if ( curr -> left ) q . push ( curr -> left ); // Enqueue right child if ( curr -> right ) q . push ( curr -> right ); // Dequeue node q . pop (); // if flag is true print leftmost node if ( flag && n == nodeCount - 1 ) cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; // if flag is false print rightmost node if ( ! flag && n == 0 ) cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; } // invert flag for next level flag = ! flag ; } } /* Driver program to test above functions */ int main () { // Binary Tree of Height 4 Node * root = newNode ( 1 ); root -> left = newNode ( 2 ); root -> right = newNode ( 3 ); root -> left -> left = newNode ( 4 ); root -> left -> right = newNode ( 5 ); root -> right -> right = newNode ( 7 ); root -> left -> left -> left = newNode ( 8 ); root -> left -> left -> right = newNode ( 9 ); root -> left -> right -> left = newNode ( 10 ); root -> left -> right -> right = newNode ( 11 ); root -> right -> right -> left = newNode ( 14 ); root -> right -> right -> right = newNode ( 15 ); root -> left -> left -> left -> left = newNode ( 16 ); root -> left -> left -> left -> right = newNode ( 17 ); root -> right -> right -> right -> right = newNode ( 31 ); printExtremeNodes ( root ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order import java.util.* ; class GFG { // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / static class Node { int data ; Node left right ; }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / static Node newNode ( int data ) { Node node = new Node (); node . data = data ; node . right = node . left = null ; return node ; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order static void printExtremeNodes ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root Queue < Node > q = new LinkedList < Node > (); q . add ( root ); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed boolean flag = false ; while ( q . size () > 0 ) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q . size (); int n = nodeCount ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( n --> 0 ) { Node curr = q . peek (); // Enqueue left child if ( curr . left != null ) q . add ( curr . left ); // Enqueue right child if ( curr . right != null ) q . add ( curr . right ); // Dequeue node q . remove (); // if flag is true print leftmost node if ( flag && n == nodeCount - 1 ) System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); // if flag is false print rightmost node if ( ! flag && n == 0 ) System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); } // invert flag for next level flag = ! flag ; } } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { // Binary Tree of Height 4 Node root = newNode ( 1 ); root . left = newNode ( 2 ); root . right = newNode ( 3 ); root . left . left = newNode ( 4 ); root . left . right = newNode ( 5 ); root . right . right = newNode ( 7 ); root . left . left . left = newNode ( 8 ); root . left . left . right = newNode ( 9 ); root . left . right . left = newNode ( 10 ); root . left . right . right = newNode ( 11 ); root . right . right . left = newNode ( 14 ); root . right . right . right = newNode ( 15 ); root . left . left . left . left = newNode ( 16 ); root . left . left . left . right = newNode ( 17 ); root . right . right . right . right = newNode ( 31 ); printExtremeNodes ( root ); } } // This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python # Python program to print nodes of extreme corners # of each level in alternate order # Utility class to create a node class Node : def __init__ ( self key ): self . data = key self . left = self . right = None # Utility function to create a tree node def newNode ( data ): temp = Node ( 0 ) temp . data = data temp . left = temp . right = None return temp # Function to print nodes of extreme corners # of each level in alternate order def printExtremeNodes ( root ): if ( root == None ): return # Create a queue and enqueue left and right # children of root q = [] q . append ( root ) # flag to indicate whether leftmost node or # the rightmost node has to be printed flag = False while ( len ( q ) > 0 ): # nodeCount indicates number of nodes # at current level. nodeCount = len ( q ) n = nodeCount # Dequeue all nodes of current level # and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( n > 0 ): n = n - 1 curr = q [ 0 ] # Enqueue left child if ( curr . left != None ): q . append ( curr . left ) # Enqueue right child if ( curr . right != None ): q . append ( curr . right ) # Dequeue node q . pop ( 0 ) # if flag is true print leftmost node if ( flag and n == nodeCount - 1 ): print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) # if flag is false print rightmost node if ( not flag and n == 0 ): print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) # invert flag for next level flag = not flag # Driver program to test above functions # Binary Tree of Height 4 root = newNode ( 1 ) root . left = newNode ( 2 ) root . right = newNode ( 3 ) root . left . left = newNode ( 4 ) root . left . right = newNode ( 5 ) root . right . right = newNode ( 7 ) root . left . left . left = newNode ( 8 ) root . left . left . right = newNode ( 9 ) root . left . right . left = newNode ( 10 ) root . left . right . right = newNode ( 11 ) root . right . right . left = newNode ( 14 ) root . right . right . right = newNode ( 15 ) root . left . left . left . left = newNode ( 16 ) root . left . left . left . right = newNode ( 17 ) root . right . right . right . right = newNode ( 31 ) printExtremeNodes ( root ) # This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
C# // C# program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GFG { // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / public class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / static Node newNode ( int data ) { Node node = new Node (); node . data = data ; node . right = node . left = null ; return node ; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order static void printExtremeNodes ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root Queue < Node > q = new Queue < Node > (); q . Enqueue ( root ); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed Boolean flag = false ; while ( q . Count > 0 ) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q . Count ; int n = nodeCount ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( n --> 0 ) { Node curr = q . Peek (); // Enqueue left child if ( curr . left != null ) q . Enqueue ( curr . left ); // Enqueue right child if ( curr . right != null ) q . Enqueue ( curr . right ); // Dequeue node q . Dequeue (); // if flag is true print leftmost node if ( flag && n == nodeCount - 1 ) Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); // if flag is false print rightmost node if ( ! flag && n == 0 ) Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); } // invert flag for next level flag = ! flag ; } } // Driver code public static void Main ( String [] args ) { // Binary Tree of Height 4 Node root = newNode ( 1 ); root . left = newNode ( 2 ); root . right = newNode ( 3 ); root . left . left = newNode ( 4 ); root . left . right = newNode ( 5 ); root . right . right = newNode ( 7 ); root . left . left . left = newNode ( 8 ); root . left . left . right = newNode ( 9 ); root . left . right . left = newNode ( 10 ); root . left . right . right = newNode ( 11 ); root . right . right . left = newNode ( 14 ); root . right . right . right = newNode ( 15 ); root . left . left . left . left = newNode ( 16 ); root . left . left . left . right = newNode ( 17 ); root . right . right . right . right = newNode ( 31 ); printExtremeNodes ( root ); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / class Node { constructor () { this . data = 0 ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / function newNode ( data ) { var node = new Node (); node . data = data ; node . right = node . left = null ; return node ; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order function printExtremeNodes ( root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root var q = []; q . push ( root ); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed var flag = false ; while ( q . length > 0 ) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. var nodeCount = q . length ; var n = nodeCount ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and push all nodes of next level while ( n --> 0 ) { var curr = q [ 0 ]; // push left child if ( curr . left != null ) q . push ( curr . left ); // push right child if ( curr . right != null ) q . push ( curr . right ); // Dequeue node q . shift (); // if flag is true print leftmost node if ( flag && n == nodeCount - 1 ) document . write ( curr . data + ' ' ); // if flag is false print rightmost node if ( ! flag && n == 0 ) document . write ( curr . data + ' ' ); } // invert flag for next level flag = ! flag ; } } // Driver code // Binary Tree of Height 4 var root = newNode ( 1 ); root . left = newNode ( 2 ); root . right = newNode ( 3 ); root . left . left = newNode ( 4 ); root . left . right = newNode ( 5 ); root . right . right = newNode ( 7 ); root . left . left . left = newNode ( 8 ); root . left . left . right = newNode ( 9 ); root . left . right . left = newNode ( 10 ); root . left . right . right = newNode ( 11 ); root . right . right . left = newNode ( 14 ); root . right . right . right = newNode ( 15 ); root . left . left . left . left = newNode ( 16 ); root . left . left . left . right = newNode ( 17 ); root . right . right . right . right = newNode ( 31 ); printExtremeNodes ( root ); < /script>
Ausgabe
1 2 7 8 31
Zeitkomplexität: O(n) wobei n die Gesamtzahl der Knoten in einem bestimmten Binärbaum ist.
Hilfsraum: O(n) wobei n die Gesamtzahl der Knoten in einem bestimmten Binärbaum aufgrund der Warteschlange ist.
Übung - Drucken Sie die Knoten der äußersten Ecken jeder Ebene von unten nach oben in abwechselnder Reihenfolge.