Matplotlib.pyplot.savefig() in Python
Matplotlib ist eine äußerst nützliche Visualisierungsbibliothek in Python. Es handelt sich um eine plattformübergreifende Datenvisualisierungsbibliothek, die auf NumPy-Arrays basiert und für die Zusammenarbeit mit dem breiteren SciPy-Stack konzipiert ist. Visualisierung spielt eine sehr wichtige Rolle, da sie uns hilft, große Datenmengen zu verstehen und Wissen zu extrahieren.
Matplotlib.pyplot.savefig()
Wie der Name schon sagt, wird die Methode savefig() verwendet, um die danach erstellte Figur zu speichern Plotten Daten. Mit dieser Methode kann die erstellte Figur auf unseren lokalen Rechnern gespeichert werden.
Syntax: savefig(fname, dpi=Keine, Gesichtsfarbe='w', Kantenfarbe='w', Ausrichtung='Porträt', Papiertyp=Keine, Format=Keine, transparent=Falsch, bbox_inches=Keine, pad_inches=0.1, Frameon=Keine, Metadaten=Keine)
Parameter:
| PARAMETER | BESCHREIBUNG | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| fname | Dateiname .webp'code-block'>
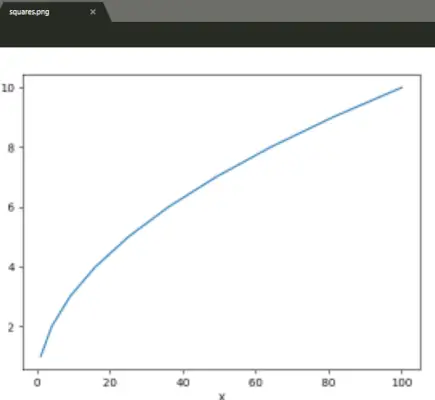
Ausgabe : Beispiel 2:
Ausgabe : |