K'th Boom-Nummer
 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; } Boom-Zahlen sind Zahlen, die nur aus den Ziffern 2 und 3 bestehen. Gegeben sei eine ganze Zahl k (0
Input : k = 2 Output: 3 Input : k = 3 Output: 22 Input : k = 100 Output: 322323 Input: k = 1000000 Output: 3332322223223222223Recommended Practice K-te Boom-Nummer Probieren Sie es aus!
Die Idee ist sehr einfach Generieren Sie Binärzahlen . Auch hier verwenden wir den gleichen Ansatz
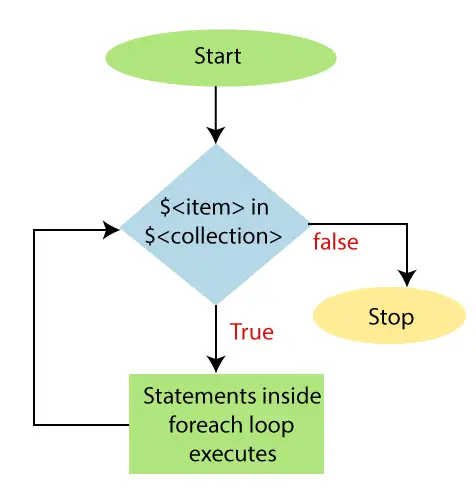
Wir verwenden die Warteschlangendatenstruktur, um dieses Problem zu lösen. Stellen Sie zuerst „2“ und dann „3“ in die Warteschlange. Diese beiden sind die erste bzw. zweite Boom-Nummer. Setzen Sie nun count=2 für jedes Mal, wenn pop() vor der Warteschlange steht, hängen Sie „2“ an die gepoppte Zahl an und erhöhen Sie count++, wenn (count==k), dann drucken Sie den aktuellen Wert Boom-Nummer andernfalls '3' an die ausgegebene Zahl anhängen und count++ erhöhen, wenn (count==k), dann aktuelle Ausgabe ausgeben Boom-Nummer . Wiederholen Sie den Vorgang, bis wir K'th erreichen Boom-Nummer .
Dieser Ansatz kann als BFS eines Baums mit der Wurzel als leerer Zeichenfolge angesehen werden. Dem linken Kind jedes Knotens ist eine 2 angehängt und dem rechten Kind ist eine 3 angehängt.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung dieser Idee.
C++ // C++ program to find K'th Boom number #include using namespace std ; typedef long long int ll ; // This function uses queue data structure to K'th // Boom number void boomNumber ( ll k ) { // Create an empty queue of strings queue < string > q ; // Enqueue an empty string q . push ( '' ); // counter for K'th element ll count = 0 ; // This loop checks the value of count to // become equal to K when value of count // will be equals to k we will print the // Boom number while ( count <= k ) { // current Boom number string s1 = q . front (); // pop front q . pop (); // Store current Boom number before changing it string s2 = s1 ; // Append '2' to string s1 and enqueue it q . push ( s1 . append ( '2' )); count ++ ; // check if count==k if ( count == k ) { cout < < s1 < < endl ; // K'th Boom number break ; } // Append '3' to string s2 and enqueue it. // Note that s2 contains the previous front q . push ( s2 . append ( '3' )); count ++ ; // check if count==k if ( count == k ) { cout < < s2 < < endl ; // K'th Boom number break ; } } return ; } // Driver program to test above function int main () { ll k = 1000000 ; boomNumber ( k ); return 0 ; }
Java /*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.* ; import java.util.* ; class GFG { // This function uses queue data structure to K'th // Boom number static void boomNumber ( long k ) { // Create an empty queue of strings Queue < String > q = new LinkedList < String > (); // Enqueue an empty string q . add ( '' ); // counter for K'th element long count = 0 ; // This loop checks the value of count to // become equal to K when value of count // will be equals to k we will print the // Boom number while ( count <= k ) { // current Boom number String s1 = q . poll (); // Store current Boom number before changing it String s2 = s1 ; // Append '2' to string s1 and enqueue it q . add ( s1 + '2' ); count ++ ; // check if count==k if ( count == k ) { System . out . println ( s1 ); // K'th Boom number break ; } // Append '3' to string s2 and enqueue it. // Note that s2 contains the previous front q . add ( s2 + '3' ); count ++ ; // check if count==k if ( count == k ) { System . out . println ( s2 ); // K'th Boom number break ; } } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { long k = 1000000 ; boomNumber ( k ); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Python3 # Python3 program to find K'th Boom number # This function uses queue data structure to K'th # Boom number def boomNumber ( k ): # Create an empty queue of strings q = [] # Enqueue an empty string q . append ( '' ) # counter for K'th element count = 0 # This loop checks the value of count to # become equal to K when value of count # will be equals to k we will print the # Boom number while ( count <= k ): # current Boom number s1 = q [ 0 ] # pop front q = q [ 1 :] # Store current Boom number before changing it s2 = s1 # Append '2' to string s1 and enqueue it s1 += '2' q . append ( s1 ) count = count + 1 # check if count==k if ( count == k ): print ( s1 ) # K'th Boom number break # Append '3' to string s2 and enqueue it. # Note that s2 contains the previous front s2 += '3' q . append ( s2 ) count = count + 1 # check if count==k if ( count == k ): print ( s2 ) # K'th Boom number break return # Driver program to test above function k = 1000000 boomNumber ( k ) # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
C# // C# program to find K'th Boom number using System ; using System.Collections ; class GFG { // This function uses queue data structure // to K'th Boom number static void boomNumber ( long k ) { // Create an empty queue of strings Queue q = new Queue (); // Enqueue an empty string q . Enqueue ( '' ); // counter for K'th element long count = 0 ; // This loop checks the value of count to // become equal to K when value of count // will be equals to k we will print the // Boom number while ( count <= k ) { // current Boom number string s1 = ( string ) q . Dequeue (); // Store current Boom number // before changing it string s2 = s1 ; // Append '2' to string s1 and // enqueue it s1 += '2' ; q . Enqueue ( s1 ); count ++ ; // Check if count==k if ( count == k ) { // K'th Boom number Console . Write ( s1 ); break ; } // Append '3' to string s2 and enqueue it. // Note that s2 contains the previous front s2 += '3' ; q . Enqueue ( s2 ); count ++ ; // Check if count==k if ( count == k ) { // K'th Boom number Console . Write ( s2 ); break ; } } return ; } // Driver code public static void Main ( string [] arg ) { long k = 1000000 ; boomNumber ( k ); } } // This code is contributed by rutvik_56
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to find K'th Boom number // This function uses queue data structure to K'th // Boom number function boomNumber ( k ){ // Create an empty queue of strings let q = [] // Enqueue an empty string q . push ( '' ) // counter for K'th element let count = 0 // This loop checks the value of count to // become equal to K when value of count // will be equals to k we will print the // Boom number while ( count <= k ){ // current Boom number let s1 = q . shift () // Store current Boom number before changing it let s2 = s1 // Append '2' to string s1 and enqueue it s1 += '2' q . push ( s1 ) count = count + 1 // check if count==k if ( count == k ){ document . write ( s1 ' ' ) // K'th Boom number break } // Append '3' to string s2 and enqueue it. // Note that s2 contains the previous front s2 += '3' q . push ( s2 ) count = count + 1 // check if count==k if ( count == k ){ document . write ( s2 ' ' ) // K'th Boom number break } } return } // Driver program to test above function let k = 1000000 boomNumber ( k ) // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra < /script>
Ausgabe
3332322223223222223
Zeitkomplexität: O(K)
Hilfsraum: O(n)
Dieser Artikel wurde vom Team GeeksforGeeks überprüft.