Implementieren einer verknüpften Liste in Java mithilfe von Class
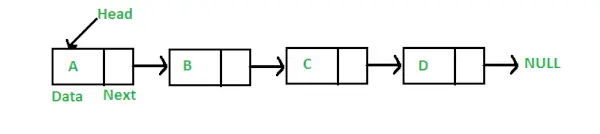
Voraussetzung: Ebenso wie Arrays ist die verknüpfte Liste eine lineare Datenstruktur. Im Gegensatz zu Arrays werden verknüpfte Listenelemente nicht an der zusammenhängenden Position gespeichert, sondern die Elemente werden mithilfe von Zeigern verknüpft, wie unten gezeigt.

In Java kann LinkedList als Klasse und Node als separate Klasse dargestellt werden. Die LinkedList-Klasse enthält eine Referenz vom Node-Klassentyp.
Java
class> LinkedList {> > Node head;> // head of list> > /* Linked list Node*/> > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node next;> > // Constructor to create a new node> > // Next is by default initialized> > // as null> > Node(> int> d) { data = d; }> > }> }> |
Erstellung und Einfügen:
In diesem Artikel erfolgt das Einfügen in die Liste am Ende, das heißt, der neue Knoten wird nach dem letzten Knoten der angegebenen verknüpften Liste hinzugefügt. Wenn die angegebene verknüpfte Liste beispielsweise 5->10->15->20->25 lautet und 30 eingefügt werden soll, wird die verknüpfte Liste zu 5->10->15->20->25->30 .
Da eine verknüpfte Liste normalerweise durch ihren Kopfzeiger dargestellt wird, ist es erforderlich, die Liste bis zum letzten Knoten zu durchlaufen und dann den vorletzten Knoten in den neuen Knoten zu ändern.

Implementierung:
Java
import> java.io.*;> > // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > > Node head;> // head of list> > > // Linked list Node.> > // This inner class is made static> > // so that main() can access it> > static> class> Node {> > > int> data;> > Node next;> > > // Constructor> > Node(> int> d)> > {> > data = d;> > next => null> ;> > }> > }> > > // Method to insert a new node> > public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> int> data)> > {> > // Create a new node with given data> > Node new_node => new> Node(data);> > > > // If the Linked List is empty,> > // then make the new node as head> > if> (list.head ==> null> ) {> > list.head = new_node;> > }> > else> {> > // Else traverse till the last node> > // and insert the new_node there> > Node last = list.head;> > while> (last.next !=> null> ) {> > last = last.next;> > }> > > // Insert the new_node at last node> > last.next = new_node;> > }> > > // Return the list by head> > return> list;> > }> > > // Method to print the LinkedList.> > public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> > {> > Node currNode = list.head;> > > System.out.print(> 'LinkedList: '> );> > > // Traverse through the LinkedList> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Print the data at current node> > System.out.print(currNode.data +> ' '> );> > > // Go to next node> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > }> > > // Driver code> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > /* Start with the empty list. */> > LinkedList list => new> LinkedList();> > > //> > // ******INSERTION******> > //> > > // Insert the values> > list = insert(list,> 1> );> > list = insert(list,> 2> );> > list = insert(list,> 3> );> > list = insert(list,> 4> );> > list = insert(list,> 5> );> > list = insert(list,> 6> );> > list = insert(list,> 7> );> > list = insert(list,> 8> );> > > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > }> }> |
Ausgabe
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Durchquerung: Zum Durchlaufen finden Sie unten eine Allzweckfunktion printList(), die eine beliebige Liste druckt, indem sie die Liste vom Kopfknoten bis zum letzten durchläuft.
Implementierung:
Java
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > Node head;> // head of list> > // Linked list Node.> > // Node is a static nested class> > // so main() can access it> > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node next;> > // Constructor> > Node(> int> d)> > {> > data = d;> > next => null> ;> > }> > }> > // Method to insert a new node> > public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> > int> data)> > {> > // Create a new node with given data> > Node new_node => new> Node(data);> > new_node.next => null> ;> > // If the Linked List is empty,> > // then make the new node as head> > if> (list.head ==> null> ) {> > list.head = new_node;> > }> > else> {> > // Else traverse till the last node> > // and insert the new_node there> > Node last = list.head;> > while> (last.next !=> null> ) {> > last = last.next;> > }> > // Insert the new_node at last node> > last.next = new_node;> > }> > // Return the list by head> > return> list;> > }> > // Method to print the LinkedList.> > public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> > {> > Node currNode = list.head;> > System.out.print(> 'LinkedList: '> );> > // Traverse through the LinkedList> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Print the data at current node> > System.out.print(currNode.data +> ' '> );> > // Go to next node> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > }> > // **************MAIN METHOD**************> > // method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > /* Start with the empty list. */> > LinkedList list => new> LinkedList();> > //> > // ******INSERTION******> > //> > // Insert the values> > list = insert(list,> 1> );> > list = insert(list,> 2> );> > list = insert(list,> 3> );> > list = insert(list,> 4> );> > list = insert(list,> 5> );> > list = insert(list,> 6> );> > list = insert(list,> 7> );> > list = insert(list,> 8> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > }> }> |
Ausgabe
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Löschung per SCHLÜSSEL:
Der Löschvorgang kann wie folgt verstanden werden:
Getan werden:
Löschen Sie bei gegebenem „Schlüssel“ das erste Vorkommen dieses Schlüssels in der verknüpften Liste .
Wie es geht:
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, um einen Knoten aus der verknüpften Liste zu löschen.
- Durchsuchen Sie den Schlüssel nach seinem ersten Vorkommen in der Liste
- Nun kann jede der drei Bedingungen vorliegen:
- Fall 1: Der Schlüssel wird am gefunden Kopf
- Ändern Sie in diesem Fall den Kopf des Knotens in den nächsten Knoten des aktuellen Kopfes.
- Geben Sie den Speicher des ersetzten Hauptknotens frei.
- Fall 2: Der Schlüssel befindet sich in der Mitte oder am Ende, außer am Kopf
- Suchen Sie in diesem Fall den vorherigen Knoten des zu löschenden Knotens.
- Ändern Sie den nächsten Knoten des vorherigen Knotens in den nächsten Knoten des aktuellen Knotens.
- Geben Sie den Speicher des ersetzten Knotens frei.
- Fall 3: Der Schlüssel wird nicht in der Liste gefunden
- In diesem Fall ist keine Operation erforderlich.

Implementierung:
Java
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > Node head;> // head of list> > // Linked list Node.> > // Node is a static nested class> > // so main() can access it> > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node next;> > // Constructor> > Node(> int> d)> > {> > data = d;> > next => null> ;> > }> > }> > // Method to insert a new node> > public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> > int> data)> > {> > // Create a new node with given data> > Node new_node => new> Node(data);> > new_node.next => null> ;> > // If the Linked List is empty,> > // then make the new node as head> > if> (list.head ==> null> ) {> > list.head = new_node;> > }> > else> {> > // Else traverse till the last node> > // and insert the new_node there> > Node last = list.head;> > while> (last.next !=> null> ) {> > last = last.next;> > }> > // Insert the new_node at last node> > last.next = new_node;> > }> > // Return the list by head> > return> list;> > }> > // Method to print the LinkedList.> > public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> > {> > Node currNode = list.head;> > System.out.print(> 'LinkedList: '> );> > // Traverse through the LinkedList> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Print the data at current node> > System.out.print(currNode.data +> ' '> );> > // Go to next node> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > System.out.println();> > }> > // **************DELETION BY KEY**************> > // Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY> > public> static> LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,> > int> key)> > {> > // Store head node> > Node currNode = list.head, prev => null> ;> > //> > // CASE 1:> > // If head node itself holds the key to be deleted> > if> (currNode !=> null> && currNode.data == key) {> > list.head = currNode.next;> // Changed head> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' found and deleted'> );> > // Return the updated List> > return> list;> > }> > //> > // CASE 2:> > // If the key is somewhere other than at head> > //> > // Search for the key to be deleted,> > // keep track of the previous node> > // as it is needed to change currNode.next> > while> (currNode !=> null> && currNode.data != key) {> > // If currNode does not hold key> > // continue to next node> > prev = currNode;> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > // If the key was present, it should be at currNode> > // Therefore the currNode shall not be null> > if> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Since the key is at currNode> > // Unlink currNode from linked list> > prev.next = currNode.next;> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' found and deleted'> );> > }> > //> > // CASE 3: The key is not present> > //> > // If key was not present in linked list> > // currNode should be null> > if> (currNode ==> null> ) {> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' not found'> );> > }> > // return the List> > return> list;> > }> > // **************MAIN METHOD**************> > // method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > /* Start with the empty list. */> > LinkedList list => new> LinkedList();> > //> > // ******INSERTION******> > //> > // Insert the values> > list = insert(list,> 1> );> > list = insert(list,> 2> );> > list = insert(list,> 3> );> > list = insert(list,> 4> );> > list = insert(list,> 5> );> > list = insert(list,> 6> );> > list = insert(list,> 7> );> > list = insert(list,> 8> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > //> > // ******DELETION BY KEY******> > //> > // Delete node with value 1> > // In this case the key is ***at head***> > deleteByKey(list,> 1> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node with value 4> > // In this case the key is present ***in the> > // middle***> > deleteByKey(list,> 4> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node with value 10> > // In this case the key is ***not present***> > deleteByKey(list,> 10> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > }> }> |
Ausgabe
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
Löschung an Position:
Dieser Löschvorgang kann wie folgt verstanden werden:
Getan werden:
Angenommen 'Position' , löschen Sie den Knoten an dieser Position aus der verknüpften Liste .
Wie es geht:
Die Schritte dazu sind wie folgt:
- Durchlaufen Sie die Liste, indem Sie den Index der Knoten zählen
- Passen Sie für jeden Index an, dass der Index mit der Position übereinstimmt
- Nun kann jede der drei Bedingungen vorliegen:
- Fall 1: Die Position ist 0, d. h. der Kopf soll gelöscht werden
- Ändern Sie in diesem Fall den Kopf des Knotens zum nächsten Knoten des aktuellen Kopfes.
- Geben Sie den Speicher des ersetzten Hauptknotens frei.
- Fall 2: Die Position ist größer als 0, aber kleiner als die Größe der Liste, d. h. in der Mitte oder am Ende, außer am Kopf
- In diesem Fall suchen Sie den vorherigen Knoten des zu löschenden Knotens.
- Ändern Sie den nächsten Knoten des vorherigen Knotens in den nächsten Knoten des aktuellen Knotens.
- Geben Sie den Speicher des ersetzten Knotens frei.
- Fall 3: Die Position ist größer als die Liste, d. h. die Position wurde in der Liste nicht gefunden
- In diesem Fall ist keine Operation erforderlich.

Implementierung:
Java
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > Node head;> // head of list> > // Linked list Node.> > // Node is a static nested class> > // so main() can access it> > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node next;> > // Constructor> > Node(> int> d)> > {> > data = d;> > next => null> ;> > }> > }> > // Method to insert a new node> > public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> > int> data)> > {> > // Create a new node with given data> > Node new_node => new> Node(data);> > new_node.next => null> ;> > // If the Linked List is empty,> > // then make the new node as head> > if> (list.head ==> null> ) {> > list.head = new_node;> > }> > else> {> > // Else traverse till the last node> > // and insert the new_node there> > Node last = list.head;> > while> (last.next !=> null> ) {> > last = last.next;> > }> > // Insert the new_node at last node> > last.next = new_node;> > }> > // Return the list by head> > return> list;> > }> > // Method to print the LinkedList.> > public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> > {> > Node currNode = list.head;> > System.out.print(> 'LinkedList: '> );> > // Traverse through the LinkedList> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Print the data at current node> > System.out.print(currNode.data +> ' '> );> > // Go to next node> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > System.out.println();> > }> > // Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION> > public> static> LinkedList> > deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list,> int> index)> > {> > // Store head node> > Node currNode = list.head, prev => null> ;> > //> > // CASE 1:> > // If index is 0, then head node itself is to be> > // deleted> > if> (index ==> 0> && currNode !=> null> ) {> > list.head = currNode.next;> // Changed head> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element deleted'> );> > // Return the updated List> > return> list;> > }> > //> > // CASE 2:> > // If the index is greater than 0 but less than the> > // size of LinkedList> > //> > // The counter> > int> counter => 0> ;> > // Count for the index to be deleted,> > // keep track of the previous node> > // as it is needed to change currNode.next> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > if> (counter == index) {> > // Since the currNode is the required> > // position Unlink currNode from linked list> > prev.next = currNode.next;> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element deleted'> );> > break> ;> > }> > else> {> > // If current position is not the index> > // continue to next node> > prev = currNode;> > currNode = currNode.next;> > counter++;> > }> > }> > // If the position element was found, it should be> > // at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be> > // null> > //> > // CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the> > // LinkedList> > //> > // In this case, the currNode should be null> > if> (currNode ==> null> ) {> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element not found'> );> > }> > // return the List> > return> list;> > }> > // **************MAIN METHOD**************> > // method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > /* Start with the empty list. */> > LinkedList list => new> LinkedList();> > //> > // ******INSERTION******> > //> > // Insert the values> > list = insert(list,> 1> );> > list = insert(list,> 2> );> > list = insert(list,> 3> );> > list = insert(list,> 4> );> > list = insert(list,> 5> );> > list = insert(list,> 6> );> > list = insert(list,> 7> );> > list = insert(list,> 8> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > //> > // ******DELETION AT POSITION******> > //> > // Delete node at position 0> > // In this case the key is ***at head***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 0> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node at position 2> > // In this case the key is present ***in the> > // middle***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 2> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node at position 10> > // In this case the key is ***not present***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 10> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > }> }> |
Ausgabe
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 0 position element deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 position element deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 position element not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
Alle Operationen:
Nachfolgend finden Sie das vollständige Programm, das jede Operation zusammen anwendet:
Java
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > Node head;> // head of list> > // Linked list Node.> > // Node is a static nested class> > // so main() can access it> > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node next;> > // Constructor> > Node(> int> d)> > {> > data = d;> > next => null> ;> > }> > }> > // **************INSERTION**************> > // Method to insert a new node> > public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> > int> data)> > {> > // Create a new node with given data> > Node new_node => new> Node(data);> > new_node.next => null> ;> > // If the Linked List is empty,> > // then make the new node as head> > if> (list.head ==> null> ) {> > list.head = new_node;> > }> > else> {> > // Else traverse till the last node> > // and insert the new_node there> > Node last = list.head;> > while> (last.next !=> null> ) {> > last = last.next;> > }> > // Insert the new_node at last node> > last.next = new_node;> > }> > // Return the list by head> > return> list;> > }> > // **************TRAVERSAL**************> > // Method to print the LinkedList.> > public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> > {> > Node currNode = list.head;> > System.out.print(> '
LinkedList: '> );> > // Traverse through the LinkedList> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Print the data at current node> > System.out.print(currNode.data +> ' '> );> > // Go to next node> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > System.out.println(> '
'> );> > }> > // **************DELETION BY KEY**************> > // Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY> > public> static> LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,> > int> key)> > {> > // Store head node> > Node currNode = list.head, prev => null> ;> > //> > // CASE 1:> > // If head node itself holds the key to be deleted> > if> (currNode !=> null> && currNode.data == key) {> > list.head = currNode.next;> // Changed head> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' found and deleted'> );> > // Return the updated List> > return> list;> > }> > //> > // CASE 2:> > // If the key is somewhere other than at head> > //> > // Search for the key to be deleted,> > // keep track of the previous node> > // as it is needed to change currNode.next> > while> (currNode !=> null> && currNode.data != key) {> > // If currNode does not hold key> > // continue to next node> > prev = currNode;> > currNode = currNode.next;> > }> > // If the key was present, it should be at currNode> > // Therefore the currNode shall not be null> > if> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > // Since the key is at currNode> > // Unlink currNode from linked list> > prev.next = currNode.next;> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' found and deleted'> );> > }> > //> > // CASE 3: The key is not present> > //> > // If key was not present in linked list> > // currNode should be null> > if> (currNode ==> null> ) {> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(key +> ' not found'> );> > }> > // return the List> > return> list;> > }> > // **************DELETION AT A POSITION**************> > // Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION> > public> static> LinkedList> > deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list,> int> index)> > {> > // Store head node> > Node currNode = list.head, prev => null> ;> > //> > // CASE 1:> > // If index is 0, then head node itself is to be> > // deleted> > if> (index ==> 0> && currNode !=> null> ) {> > list.head = currNode.next;> // Changed head> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element deleted'> );> > // Return the updated List> > return> list;> > }> > //> > // CASE 2:> > // If the index is greater than 0 but less than the> > // size of LinkedList> > //> > // The counter> > int> counter => 0> ;> > // Count for the index to be deleted,> > // keep track of the previous node> > // as it is needed to change currNode.next> > while> (currNode !=> null> ) {> > if> (counter == index) {> > // Since the currNode is the required> > // position Unlink currNode from linked list> > prev.next = currNode.next;> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element deleted'> );> > break> ;> > }> > else> {> > // If current position is not the index> > // continue to next node> > prev = currNode;> > currNode = currNode.next;> > counter++;> > }> > }> > // If the position element was found, it should be> > // at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be> > // null> > //> > // CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the> > // LinkedList> > //> > // In this case, the currNode should be null> > if> (currNode ==> null> ) {> > // Display the message> > System.out.println(> > index +> ' position element not found'> );> > }> > // return the List> > return> list;> > }> > // **************MAIN METHOD**************> > // method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > /* Start with the empty list. */> > LinkedList list => new> LinkedList();> > //> > // ******INSERTION******> > //> > // Insert the values> > list = insert(list,> 1> );> > list = insert(list,> 2> );> > list = insert(list,> 3> );> > list = insert(list,> 4> );> > list = insert(list,> 5> );> > list = insert(list,> 6> );> > list = insert(list,> 7> );> > list = insert(list,> 8> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > //> > // ******DELETION BY KEY******> > //> > // Delete node with value 1> > // In this case the key is ***at head***> > deleteByKey(list,> 1> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node with value 4> > // In this case the key is present ***in the> > // middle***> > deleteByKey(list,> 4> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node with value 10> > // In this case the key is ***not present***> > deleteByKey(list,> 10> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > //> > // ******DELETION AT POSITION******> > //> > // Delete node at position 0> > // In this case the key is ***at head***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 0> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node at position 2> > // In this case the key is present ***in the> > // middle***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 2> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > // Delete node at position 10> > // In this case the key is ***not present***> > deleteAtPosition(list,> 10> );> > // Print the LinkedList> > printList(list);> > }> }> |
Ausgabe
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 0 position element deleted LinkedList: 3 5 6 7 8 2 position element deleted LinkedList: 3 5 7 8 10 position element not found LinkedList: 3 5 7 8