Finden Sie alle Binärsequenzen gerader Länge mit der gleichen Summe der ersten und zweiten Halbbits
Finden Sie bei einer gegebenen Zahl n alle binären Folgen der Länge 2n, sodass die Summe der ersten n Bits mit der Summe der letzten n Bits übereinstimmt.
Beispiele:
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
Die Idee besteht darin, das erste und das letzte Bit zu korrigieren und es dann für die verbleibenden 2*(n-1) Bits zu wiederholen. Es gibt vier Möglichkeiten, wenn wir das erste und das letzte Bit reparieren:
- Erstes und letztes Bit sind 1, die restlichen n – 1 Bits auf beiden Seiten sollten ebenfalls die gleiche Summe haben.
- Erstes und letztes Bit sind 0, die restlichen n-1 Bits auf beiden Seiten sollten ebenfalls die gleiche Summe haben.
- Das erste Bit ist 1 und das letzte Bit ist 0. Die Summe der verbleibenden n-1 Bits auf der linken Seite sollte um 1 kleiner sein als die Summe der n-1 Bits auf der rechten Seite.
- Das erste Bit ist 0 und das letzte Bit ist 1. Die Summe der verbleibenden n-1 Bits auf der linken Seite sollte um 1 größer sein als die Summe der n-1 Bits auf der rechten Seite.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung der oben genannten Idee:
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include using namespace std ; // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index void findAllSequences ( int diff char * out int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) cout < < out < < ' ' ; return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program int main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char out [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.* ; import java.util.* ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char out [] int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { System . out . print ( out ); System . out . print ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void main ( String [] args ) { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char [] out = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
Python3 # Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences ( diff out start end ): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) // 2 ): return ; # if all bits are filled if ( start > end ): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ): print ( '' . join ( list ( out )) end = ' ' ); return ; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # Driver program # input number n = 2 ; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out = [ '' ] * ( 2 * n ); findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); # This code is contributed by mits
C# // C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char [] outt int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . Abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { Console . Write ( outt ); Console . Write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char [] outt = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
PHP // PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start $end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( $diff ) > ( int )(( $end - $start + 1 ) / 2 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( $start > $end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( $diff == 0 ) print ( implode ( '' $out ) . ' ' ); return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out [ $start ] = '0' ; $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out [ $start ] = '1' ; $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out = array_fill ( 0 2 * $n '' ); findAllSequences ( 0 $out 0 2 * $n - 1 ); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?>
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( diff outt start end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > parseInt (( end - start + 1 ) / 2 10 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { document . write ( outt . join ( '' )); document . write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // input number let n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array ( 2 * n + 1 ); // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); < /script>
Ausgabe
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Zeitkomplexität: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N wegen 4 rekursiven Aufrufen und N (vereinfacht von 2N) für die Zeit, die für das Drucken von Zeichenfolgen der Größe 2N aufgewendet wurde
Hilfsraum: AN)
Es gibt einen anderen Ansatz, bei dem wir alle möglichen Zeichenfolgen der Länge n generieren und sie in einer Liste mit einem Index speichern, der ihre Summe darstellt. Dann durchlaufen wir jede Liste und generieren die Zeichenfolgen der Größe 2n, indem wir jede Zeichenfolge drucken, wobei alle anderen Zeichenfolgen in der Liste zusammen denselben Wert ergeben.
C++ // C++ program to implement the approach #include using namespace std ; //function that generates the sequence void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n vector < vector < string > >& sumToString vector < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } vector < string > x = sumToString [ sumSoFar ]; x . push_back ( seq ); sumToString [ sumSoFar ] = x ; return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push_back ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push_back ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); } // function to form permutations of the sequences void permuteSequences ( vector < vector < string > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 ) { cout < < '1111 ' ; } else { cout < < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence2 ] < < ' ' ; } } } } } // function that finds all the subsequences void findAllSequences ( int n ) { vector < vector < string > > sumToString ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push_back ( vector < string > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString vector < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } // Driver Code int main () { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); return 0 ; } // this code is contributed by phasing17
Java // Java program to implement the approach import java.util.* ; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString = new ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . add ( new ArrayList < String > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new ArrayList < String > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ArrayList < String > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence . get ( i ); } ArrayList < String > x = sumToString . get ( sumSoFar ); x . add ( seq ); sumToString . set ( sumSoFar x ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences ( ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 ) { System . out . print ( '1111' ); } else { System . out . println ( sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence1 ) + sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence2 )); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
Python3 def findAllSequences ( n ): sumToString = [[] for x in range ( n + 1 )] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ) permuteSequences ( sumToString ) def generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0 : sumToString [ sumSoFar ] . append ( '' . join ( sequence )) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence . append ( '0' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) sequence . pop () #Generate sequence +1 sequence . append ( '1' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ) sequence . pop () def permuteSequences ( sumToString ): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString : # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr : for sequence2 in sumIndexArr : print ( sequence1 + sequence2 ) findAllSequences ( 2 ) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GFG { static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { List < List < string >> sumToString = new List < List < string >> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . Add ( new List < string > ()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new List < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n List < List < string >> sumToString List < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . Count ; i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. Add ( seq ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . Add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . Add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); } static void permuteSequences ( List < List < string >> sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . Count ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . Count - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 ) { Console . Write ( '1111' ); } else { Console . WriteLine ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ]); } } } } } static void Main () { findAllSequences ( 2 ); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
JavaScript < script > function findAllSequences ( n ) { let sumToString = []; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push ([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } function generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. push ( sequence . join ( '' )); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . shift (); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . shift (); } function permuteSequences ( sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( let sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . length ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( let sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( let sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . length - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 ) { document . write ( '1111' ); } else { document . write ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ] + ' ' ); } } } } } findAllSequences ( 2 ); // This code is contributed by decode2207. < /script>
Ausgabe
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Zeitkomplexitätsanalyse:
generierenSequencesWithSum = O((2 N )*N)
- 2 N : Wir generieren alle Permutationen binärer Zeichenfolgen der Größe N
- N: Konvertieren Sie die Zeichenliste in eine Zeichenfolge und speichern Sie sie in einem Array. Dies erfolgt im Basisfall.
permuteSequences = O((2 N ) * N!/(N/2)! 2 * N)
- 2 N : Wir durchlaufen alle generierten Zeichenfolgen der Größe n
- N!/(N/2)! 2 : Das ist etwas schwierig zu erklären
Nehmen wir als Beispiel N = 2. Unser Array möglicher Folgen der Größe n wäre:
| Array-Index | 1 | 2 | |
| Liste der Zeichenfolgen | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
In der Liste der Zeichenfolgen, deren Index die Summe darstellt, erhalten wir die Anzahl der Zeichenfolgen der Größe 2n mithilfe der Formel „n wähle k“. In unserem Fall wäre es nCk *nCk, wobei k die Anzahl der Einsen in jeder Hälfte der Zeichenfolge der Größe 2n darstellt:
k = 0 wir haben (2C0)^2 = 1 String (0000)
k = 1 wir haben (2C1)^2 string = 4 strings(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 wir haben (2c2)^2 = 1 string (1111)
Wir erhalten unsere längste Liste von Zeichenfolgen, wenn k = N/2 ist N C N/2 = N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] was sich vereinfacht zu N C N/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2
Daher müssen wir für jedes Element höchstens iterieren N C N/2 zur Bildung von Saiten der Länge 2N
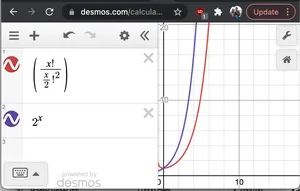
Ohne formalen Beweis, wenn wir 2^N und N!/(N/2)! grafisch darstellen 2 wir sehen das 2 N hat eine schnellere Wachstumsrate als letzteres. Deshalb O(2 N * N!/(N/2) 2 ) < O(2 N *2 N ) = O(2 2n ) = O(4 N )
 Diagramm von 2^x und nC(n/2)
Diagramm von 2^x und nC(n/2) - N: Wir müssen jede Zeichenfolge der Größe 2N drucken
Schließlich können wir die zeitliche Komplexität von „generateSequencesWithSum“ ignorieren, da „permuteSequence“ der führende Begriff ist
Zeitkomplexität: O(2 N * N!/(N/2)! 2 * N) (besser als die erste Lösung von O((4^N) * N, siehe Erklärung oben für weitere Details)
Hilfsraum : O(2 N ), weil wir alle binären String-Permutationen der Größe N speichern
#include using namespace std ; class FirstHalf { public : string data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this -> data = data ; this -> sum = sum ; } }; // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map < int vector < string >> mp ; // first N-half bits vector < FirstHalf > firstHalf ; // function to find sum of the bits from a String int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( auto c : s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } void perm ( string p char * bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push_back ( FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value mp [ sum ]. push_back ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level -1 n ); } } void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( auto first : firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key vector < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; for ( auto second : secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print cout < < first . data + second < < ' ' ; // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) cout < < endl ; } } } int main (){ char up [ 2 ] = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); return 0 ; } // This code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
Java import java.util.* ; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( String data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map < Integer ArrayList < String >> map = new HashMap <> (); //first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new ArrayList <> (); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString ( String s ) { int sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( char c : s . toCharArray ()) { sum += c - '0' ; } return sum ; } public static void perm ( String p char [] bin int level int n ) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map . putIfAbsent ( sum new ArrayList < String > ()); map . get ( sum ). add ( p ); return ; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( char c : bin ) { perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } public static void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( FirstHalf first : firstHalf ) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList < String > secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( String second : secondHalf ) { //append first and second half and print System . out . print ( first . data + second + ' ' ); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) System . out . println (); } } } public static void main ( String [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result (); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
Python3 # Python code implementation class FirstHalf : def __init__ ( self data sum ): self . data = data self . sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString ( s ): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range ( len ( s )): sum += ord ( s [ i ]) - ord ( '0' ) return sum def perm ( p bin level n ): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0 : # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString ( p ) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . append ( FirstHalf ( p sum )) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map : map [ sum ] = [] map [ sum ] . append ( p ) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range ( len ( bin )): perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ) def result (): i = 0 for j in range ( len ( firstHalf )): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf [ j ] . sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map [ sum ] for k in range ( len ( secondHalf )): # append first and second half and print print ( firstHalf [ j ] . data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' end = '' ) # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if ( i % 6 == 0 ): print ( ' n ' ) up = [ '0' '1' ] n = 2 perm ( '' up n n ) result () # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class FirstHalf { public string data ; public int sum ; public FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary < int List < string >> mp = new Dictionary < int List < string >> (); // first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new List < FirstHalf > (); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach ( char c in s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } static void perm ( string p char [] bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . Add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( mp . ContainsKey ( sum )) { mp [ sum ]. Add ( p ); } else { mp . Add ( sum new List < string > { p }); } return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } static void result () { int i = 0 ; foreach ( FirstHalf first in firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; foreach ( string second in secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print Console . Write ( first . data + second + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) Console . WriteLine (); } } } static void Main ( string [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); } }
JavaScript class FirstHalf { constructor ( data sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map (); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString ( s ) { let sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( let i = 0 ; i < s . length ; i ++ ) { sum += s . charCodeAt ( i ) - '0' . charCodeAt ( 0 ); } return sum ; } function perm ( p bin level n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( ! map . has ( sum )) map . set ( sum []); map . get ( sum ). push ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( let i = 0 ; i < bin . length ; i ++ ) { perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ); } } function result () { let i = 0 ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < firstHalf . length ; j ++ ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf [ j ]. sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( let k = 0 ; k < secondHalf . length ; k ++ ) { // append first and second half and print process . stdout . write ( firstHalf [ j ]. data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) process . stdout . write ( 'n' ); } } } const up = [ '0' '1' ]; const n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result ();
Ausgabe
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algorithmus:
1. Generieren Sie alle binären Permutationen der Größe n
2. Berechnen Sie die Summe der Bits jeder Permutation und merken Sie sie sich für die zweite Hälfte
[Beispiel: Für n=2 denken Sie daran, dass es zwei Zeichenfolgen mit der Summe = 1 gibt, d. h. „01“ „10“]
3. Iterieren Sie alle generierten Permutationen und hängen Sie für jede von ihnen die zweite Hälfte entsprechend der Summe der Bits an
Zeitkomplexitätsanalyse:
sumOfString() = O(N): Jedes Bit durchlaufen und zur Summe addieren
Dauerwelle() = O(2 N * N)
2N * N: Wir generieren alle Permutationen binärer Bits der Größe N und ermitteln die Summe der Bits für jede Permutation
Ergebnis() = O((2 N ) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2 N : Wir durchlaufen alle möglichen Permutationen der Größe N (erste Hälfte)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2 : (maximale Größe der zweiten Hälfte): Erklärung unten:
Nehmen wir als Beispiel N = 4:
//Hash-Map sieht aus wie
0 -> [0000] ................................(Listengröße: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................(Listengröße: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................(Listengröße: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................(Listengröße: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................(Listengröße: 4C4 = 1)
Wir stellen hier fest, dass jede Liste eine Größe von N wähle Schlüssel hat, die bei N wähle N/2 maximal ist
Da wir alle 2 iterieren N Permutationen und Anhängen der zweiten Hälfte der Karte. Die Karte hat die maximale Listengröße an der N/2-Position.
Der schlimmste Fall tritt in der N/2-Position auf, wo wir NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)! durchlaufen müssen. 2 Permutationen.
Zeitkomplexität: O(2 N * N!/(N/2)! 2 )
Hilfsraum: O(2 N ) weil wir alle binären String-Permutationen der Größe N speichern