Java.io.PipedOutputStream-klasse i Java

Java.io.PipedInputStream klasse i Java

Rør i IO giver et link mellem to tråde, der kører i JVM på samme tid. Så rør bruges både som kilde eller destination.
- PipedInputStream er også forbundet med PipedOutputStream. Så data kan skrives ved hjælp af PipedOutputStream og kan skrives ved hjælp af PipedInputStream. Men at bruge begge tråde på samme tid vil skabe en dødvande for trådene.
- PipedOutputStream sender enden af røret. Data skrives til PipedOutputStream. Røret siges at være brudt, hvis PipedInputStream, der læste dataene, ikke er mere.
Erklæring:
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Konstruktør:
- PipedOutputStream() : opretter en PipedOutputStream, som den ikke er tilsluttet.
- PipedOutputStream(PipedOutputStream inStream): opretter en PipedOutputStream, at den
er forbundet til PipedInputStream - 'inStream'.
Metoder:
write() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(int byte) skriver en specificeret byte til Piped Output Stream.
Syntaks:
public void write(int byte)
Parameters :
byte : byte to be written
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.skriv(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen): java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) skriver maxlen bytes af dataene fra buffer til den rørførte udgangsstrøm. Metoden blokerer, hvis der ikke skrives bytes til strømmen.
Syntaks:
public void write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : data of the buffer
offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'.
maxlen : maximum length of array to be read
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. JavaProduktion:
Use of write(buffer offset maxlen) : J A V A
- close() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.close() lukker Piped Output Stream og frigiver de allokerede ressourcer.
Syntaks:
public void close()
Parameters :
--------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- connect(PipedInputStream-destination): java.io.PipedOutputStream.connect(PipedInputStream-destination forbinder Piped Output Stream til 'destination' Piped Input Stream, og i tilfælde af at 'destination' er rør med en anden stream IO undtagelse kastes
Syntaks:
public void connect(PipedInputStream destination)
Parameters :
destination : the Piped Input Stream to be connected to
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- flush(): java.io.PipedOutputStream.flush() skyller udgangsstrømmen.
Syntaks:
public void flush()
Parameters :
------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
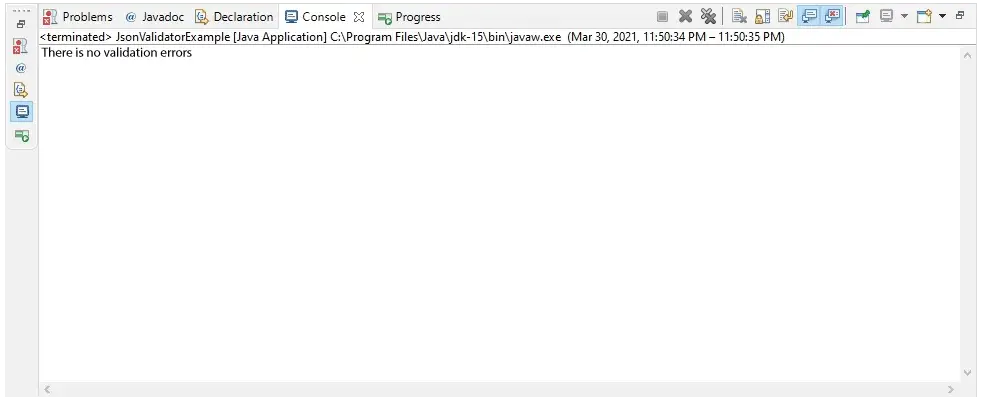
Java-kode, der illustrerer arbejdet med PipedOutputStream-klassemetoder:
JavaProduktion:
Use of flush() method :
G E E K S
Closing the Output stream
Opret Quiz