Java.io.LineNumberInputStream-klasse i Java
java.io.LineNumberInputStream-klassen er simpelthen en udvidelse af input-strømmen, der giver en ekstra mulighed for at opbevare det aktuelle linjenummer.
Linje er en sekvens af bytes, der slutter med: 'r', dvs. et vognreturtegn eller et linjeskifttegn : 'n' eller et linjeskifttegn efter vognreturtegnet.
Erklæring:
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Konstruktører:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
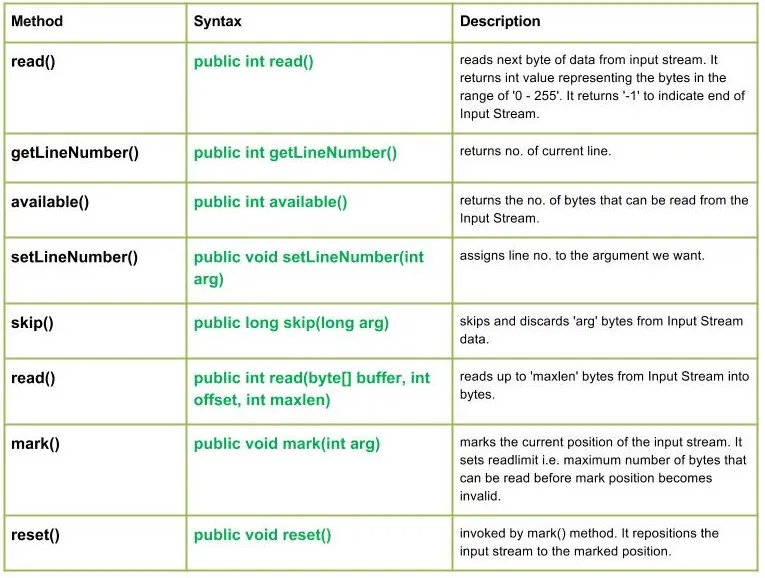
Metoder:
Syntaks:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Output:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Syntaks:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' At line : ' + a ); System . out . print ( c ); } a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' at line: ' + a ); } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
no. of lines
Output:
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Syntaks:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline . available (); System . out . println ( c + ' Bytes available : ' + a ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
available
Output:
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Syntaks:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline . setLineNumber ( 100 + b ); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a ); b ++ ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
LineNumber
Output:
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Syntaks:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline . skip ( 3 ); System . out . println ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Output: '
P r E a n k ) t
Syntaks:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementering:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Den følgende Java-kode vil ikke køre her, da vi ikke kan få adgang til nogen filer på online IDE.
Så kopier programmet til dit system og kør det der.
De ABC.txt fil brugt i programmet indeholder:
Read() method
hvad metoden gør er offset = r og maxlen = 5... så ---dvs. 3 offset derefter 5 bytes dvs. Læs (så igen offset så --
Output:
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Syntaks:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Syntaks:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
Java-program, der forklarer LineNumberInputStream-klassemetoder: reset() og mark()
Java // Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geek = null ; try { geek = new FileInputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geek ); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline . mark ( 0 ); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline . skip ( 1 ); System . out . println ( 'skip() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'mark() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); boolean check = geekline . markSupported (); if ( geekline . markSupported ()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline . reset (); System . out . println ( 'reset() invoked' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); } else { System . out . println ( 'reset() method not supported.' ); } System . out . println ( 'geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check ); } catch ( Exception except ) { // in case of I/O error except . printStackTrace (); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if ( geek != null ) geek . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Bemærk:
Denne kode vil ikke køre på online IDE, da der ikke findes en sådan fil her.
Du kan køre denne kode på dit system for at kontrollere, at det fungerer.
ABC.txt fil brugt i koden har
HelloGeeks
Output:
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false