Combinatorial Game Theory | Set 4 (Sprague - Grundy sætning)
Forudsætninger: Grundy Numbers/Numbers og Mex
Vi har allerede set i sæt 2 (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/combinatorial-game-teory-set-2-mspil-nim/), som vi kan finde, hvem der vinder i et spil NIM uden faktisk at spille spillet.
Antag, at vi ændrer det klassiske NIM -spil lidt. Denne gang kan hver spiller kun fjerne 1 2 eller 3 sten (og ikke et antal sten som i det klassiske spil Nim). Kan vi forudsige, hvem der vinder?
Ja, vi kan forudsige vinderen ved hjælp af Sprague-Grundy-sætning.
Hvad er Sprague-Grundy sætning?
Antag, at der er et sammensat spil (mere end et underspil), der består af N-underspil, og to spillere A og B. Derefter siger Sprague-Grundy-sætning, at hvis både A og B spiller optimalt (dvs. de ikke begår nogen fejl), er spilleren, der først er garanteret, at vinde, hvis Xor for grundnumrene i position i hver underspil i begyndelsen af spillet ikke er ikke-zo. Ellers hvis XOR evalueres til nul, mister spiller A bestemt uanset hvad.
Hvordan anvendes Sprague Grundy -sætning?
Vi kan anvende Sprague-Grundy-sætning i enhver Impartielt spil og løse det. De grundlæggende trin er anført som følger:
- Bryd det sammensatte spil i underspil.
- Beregn derefter for hver underspil Grundy-nummeret på denne position.
- Beregn derefter XOR for alle de beregnede Grundy -numre.
- Hvis XOR-værdien er ikke-nul, vil den spiller, der skal dreje (første spiller), vinde ellers er han bestemt til at miste uanset hvad.
Eksempel Spil: Spillet starter med, at 3 bunker har 3 4 og 5 sten, og spilleren til at flytte kan tage ethvert positivt antal sten op til 3 kun fra nogen af bunkerne [forudsat at bunken har så meget mængde sten]. Den sidste spiller, der flytter, vinder. Hvilken spiller vinder spillet under forudsætning af, at begge spillere spiller optimalt?
Hvordan kan man fortælle, hvem der vinder ved at anvende Sprague-Grundy-sætning?
Som vi kan se, at dette spil i sig selv er sammensat af flere underspil.
Første trin: Underspil kan betragtes som hver bunker.
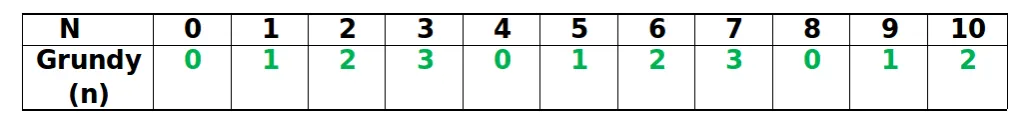
Andet trin: Vi ser fra nedenstående tabel det
Grundy(3) = 3 Grundy(4) = 0 Grundy(5) = 1

Vi har allerede set, hvordan man beregner Grundy -numrene på dette spil i tidligere Artikel.
Tredje trin: XOR på 3 0 1 = 2
Fjerde trin: Da XOR er et ikke-nul-nummer, så vi kan sige, at den første spiller vinder.
Nedenfor er det program, der implementerer over 4 trin.
C++ /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ #include using namespace std ; /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ #define PLAYER1 1 #define PLAYER2 2 // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set int calculateMex ( unordered_set < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . find ( Mex ) != Set . end ()) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy []) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != -1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); unordered_set < int > Set ; // A Hash Table for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . insert ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); } return ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main () { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = sizeof ( piles ) / sizeof ( piles [ 0 ]); // Find the maximum element int maximum = * max_element ( piles piles + n ); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [ maximum + 1 ]; memset ( Grundy -1 sizeof ( Grundy )); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ return ( 0 ); }
Java import java.util.* ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; static int PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < Integer > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy [] ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ] ); // A Hash Table HashSet < Integer > Set = new HashSet < Integer > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ] ); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]] ; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]] ; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = Arrays . stream ( piles ). max (). getAsInt (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [] = new int [ maximum + 1 ] ; Arrays . fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3 ''' Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing''' PLAYER1 = 1 PLAYER2 = 2 # A Function to calculate Mex of all # the values in that set def calculateMex ( Set ): Mex = 0 ; while ( Mex in Set ): Mex += 1 return ( Mex ) # A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' def calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ): Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ): return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A Hash Table Set = set () for i in range ( 1 4 ): Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )) # Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ) return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A function to declare the winner of the game def declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ): xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for i in range ( 1 n ): xorValue = ( xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]) if ( xorValue != 0 ): if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : # Test Case 1 piles = [ 3 4 5 ] n = len ( piles ) # Find the maximum element maximum = max ( piles ) # An array to cache the sub-problems so that # re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided Grundy = [ - 1 for i in range ( maximum + 1 )]; # Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for i in range ( n ): calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); ''' Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); ''' # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; using System.Collections.Generic ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; //static int PLAYER2 = 2; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . Contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int [] Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table HashSet < int > Set = new HashSet < int > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . Add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int [] piles int [] Grundy int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code static void Main () { // Test Case 1 int [] piles = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . Length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = piles . Max (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int [] Grundy = new int [ maximum + 1 ]; Array . Fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by mits
JavaScript < script > /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ let PLAYER1 = 1 ; let PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set function calculateMex ( Set ) { let Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . has ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' function calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table let Set = new Set (); for ( let i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game function declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ) { let xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); } return ; } // Driver code // Test Case 1 let piles = [ 3 4 5 ]; let n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element let maximum = Math . max (... piles ) // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided let Grundy = new Array ( maximum + 1 ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maximum + 1 ; i ++ ) Grundy [ i ] = 0 ; // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( let i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 < /script>
Output:
Player 1 will win
Tidskompleksitet: O (n^2) hvor n er det maksimale antal sten i en bunke.
Rumkompleksitet: O (n) Da Grundy -arrayet bruges til at gemme resultaterne af underproblemer for at undgå overflødige beregninger, og det tager O (n) plads.
Referencer:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sprague%E2%80%93grundy_theorem
Træning til læserne: Overvej nedenstående spil.
Et spil spilles af to spillere med N heltal A1 A2 .. An. På hans/hendes tur vælger en spiller, at et heltal deler den med 2 3 eller 6 og tager derefter gulvet. Hvis heltalet bliver 0, fjernes det. Den sidste spiller, der flytter, vinder. Hvilken spiller vinder spillet, hvis begge spillere spiller optimalt?
Tip: Se eksemplet 3 af tidligere Artikel.