Kontroller par med et givet produkt


Givet en matrix arr [] af n særskilte heltal og en mål Værdi Opgaven er at kontrollere, om der er et par elementer i matrixen, hvis produkt er lig med målet.
Eksempler:
Input: ARR [] = [1 5 7 -1 5] Mål = 35
Produktion: ægte
Forklaring: Som 5* 7 = 35 er svaret sandt.Input: arr [] = [-10 20 9 -40] mål = 30
Produktion: falsk
Forklaring: Intet par findes med produkt 30
Indholdstabel
- [Naiv tilgang] Ved at generere alle mulige par - O (n^2) tid og O (1) plads
- [Bedre tilgang] Brug af to markørteknik - o (n log (n)) tid og o (1) plads
- [Forventet tilgang] Brug af hashset - o (n) Tid og O (n) plads
[Naiv tilgang] ved at generere alle mulige par - O (n 2 ) tid og o (1) plads
C++Den meget basale tilgang er at generere alle mulige par og kontrollere, om der findes noget par, hvis produkt er lig med den givne målværdi og derefter returnerer ægte . Hvis der ikke findes et sådant par, skal du vende tilbage falsk .
#include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { int n = arr . size (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( 1L L * arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
C #include #include // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target bool isProduct ( int arr [] int n long long target ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( 1L L * arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } int main () { int arr [] = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; int n = sizeof ( arr ) / sizeof ( arr [ 0 ]); printf ( '%d n ' isProduct ( arr n target )); return 0 ; }
Java class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { int n = arr . length ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if (( long ) arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product # equals the target def is_product ( arr target ): n = len ( arr ) for i in range ( n - 1 ): for j in range ( i + 1 n ): if arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target : return True return False arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( is_product ( arr target ))
C# using System ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target static bool IsProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { int n = arr . Length ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if (( long ) arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } static void Main () { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( IsProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target function isProduct ( arr target ) { let n = arr . length ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] === target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
Produktion
1
Tidskompleksitet: O (n²) til brug af to indlejrede løkker
Hjælprum: O (1)
[Bedre tilgang] Brug af to markørteknik - o (n log (n)) tid og o (1) plads
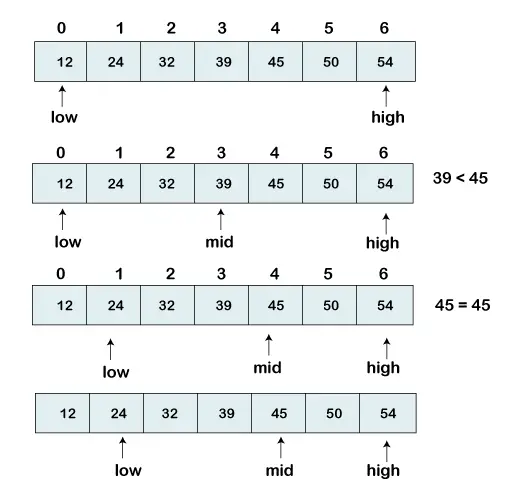
C++Vi kan også bruge to-pointer-teknikken til dette problem, men det gælder kun for sorterede data. Så sorter først matrixen og hold to pointer en markør i starten ( venstre ) og en anden i slutningen ( højre ) af arrayet. Kontroller derefter produktet af elementerne på disse to tip:
- Hvis produktet er lig med mål Vi har fundet parret.
- Hvis produktet er mindre end mål Flyt venstre markør til højre at øge produktet.
- Hvis produktet er større end mål Flyt højre markør til venstre for at reducere produktet.
#include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { // Sort the array sort ( arr . begin () arr . end ()); int left = 0 right = arr . size () - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long long currProd = 1L L * arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
C #include #include #include // Function to compare two integers (used in qsort) int compare ( const void * a const void * b ) { return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. bool isProduct ( int arr [] int n long long target ) { // Sort the array qsort ( arr n sizeof ( int ) compare ); int left = 0 right = n - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long long currProd = ( long long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } int main () { int arr [] = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; int n = sizeof ( arr ) / sizeof ( arr [ 0 ]); printf ( '%d n ' isProduct ( arr n target )); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Sort the array Arrays . sort ( arr ); int left = 0 right = arr . length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long currProd = ( long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ] ; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. def isProduct ( arr target ): # Sort the array arr . sort () left right = 0 len ( arr ) - 1 while left < right : # Calculate the current product currProd = arr [ left ] * arr [ right ] # If the product matches the target return True. if currProd == target : return True # Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if currProd > target : right -= 1 else : left += 1 return False if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( isProduct ( arr target ))
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static bool isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Sort the array Array . Sort ( arr ); int left = 0 right = arr . Length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long currProd = ( long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. function isProduct ( arr target ) { // Sort the array arr . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); let left = 0 right = arr . length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product let currProd = arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd === target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
Produktion
1
Tidskompleksitet: O (n log (n)) til sortering af matrixen
Hjælprum: O (1)
[Forventet tilgang] Brug af hashset - o (n) Tid og O (n) plads
C++Vi kan bruge en hash sæt for effektivt at se op. Når vi itererer gennem matrixen, kontrollerer vi, om hvert tal er en faktor for målet. Hvis det er, ser vi, om dens tilsvarende faktor allerede er i sættet. I så fald vender vi tilbage ægte ; Ellers tilføjer vi det aktuelle nummer til sættet og fortsætter.
#include #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { // Use an unordered set to store previously seen numbers. unordered_set < int > st ; for ( int num : arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = target / num ; // If the secondNum has been seen before return true. if ( st . find ( secondNum ) != st . end ()) { return true ; } // Mark the current number as seen. st . insert ( num ); } } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.HashSet ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Use a hash set to store previously seen numbers. HashSet < Integer > set = new HashSet <> (); for ( int num : arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 // return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of // the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = ( int )( target / num ); // If the secondNum has been seen before // return true. if ( set . contains ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. set . add ( num ); } } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. def isProduct ( arr target ): # Use a set to store previously seen numbers. st = set () for num in arr : # If target is 0 and current number is 0 return True. if target == 0 and num == 0 : return True # Check if current number can be a factor of the target. if target % num == 0 : secondNum = target // num # If the secondNum has been seen before return True. if secondNum in st : return True # Mark the current number as seen. st . add ( num ) return False if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( isProduct ( arr target ))
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static bool isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Use a hash set to store previously seen numbers. HashSet < int > set = new HashSet < int > (); foreach ( int num in arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 // return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of // the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = ( int )( target / num ); // If the secondNum has been seen before // return true. if ( set . Contains ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. set . Add ( num ); } } return false ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals // the target. function isProduct ( arr target ) { // Use a set to store previously seen numbers. let seen = new Set (); for ( let num of arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 return // true. if ( target === 0 && num === 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of the // target. if ( target % num === 0 ) { let secondNum = target / num ; // If the secondNum has been seen before return // true. if ( seen . has ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. seen . add ( num ); } } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
Produktion
1
Tidskompleksitet: O (n) til enkelt iteration
Hjælprum: O (n) Til opbevaring af elementer i hashsættet