Steinův algoritmus pro nalezení GCD

Steinův algoritmus nebo binární GCD algoritmus je algoritmus, který počítá největšího společného dělitele dvou nezáporných celých čísel. Steinův algoritmus nahrazuje dělení aritmetickými posuny porovnáváním a odečítáním.
Příklady:
Vstup : a = 17 b = 34
Výstup : 17
Vstup : a = 50 b = 49
Výstup : 1
Algoritmus k nalezení GCD pomocí Steinova algoritmu gcd(a b)
Algoritmus je především optimalizací oproti standardu Euklidovský algoritmus pro GCD
- Pokud jsou obě a i b 0, gcd je nula, gcd(0 0) = 0.
- gcd(a 0) = a a gcd(0 b) = b, protože vše dělí 0.
- Jestliže a a b jsou oba sudé, gcd(a b) = 2*gcd(a/2 b/2), protože 2 je společný dělitel. Násobení 2 lze provést pomocí operátoru bitového posunu.
- Je-li a sudé a b liché, gcd(a b) = gcd(a/2 b). Podobně je-li a liché a b je sudé tehdy
gcd(a b) = gcd(a b/2). Je to proto, že 2 není společný dělitel. - Pokud jsou obě a a b liché, pak gcd(a b) = gcd(|a-b|/2 b). Všimněte si, že rozdíl dvou lichých čísel je sudý
- Opakujte kroky 3–5, dokud a = b nebo dokud a = 0. V obou případech je GCD výkon (2 k) * b, kde výkon (2 k) je 2 zvýšení na mocninu k a k je počet společných faktorů 2 nalezených v kroku 3.
// Iterative C++ program to // implement Stein's Algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm int gcd ( int a int b ) { /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; /*Finding K where K is the greatest power of 2 that divides both a and b. */ int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } /* Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd */ while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; /* From here on 'a' is always odd. */ do { /* If b is even remove all factor of 2 in b */ while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ) swap ( a b ); // Swap u and v. b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code int main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; printf ( 'Gcd of given numbers is %d n ' gcd ( a b )); return 0 ; }
Java // Iterative Java program to // implement Stein's Algorithm import java.io.* ; class GFG { // Function to implement Stein's // Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd. do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; // Now a and b are both odd. Swap // if necessary so a <= b then set // b = b - a (which is even) if ( a > b ) { // Swap u and v. int temp = a ; a = b ; b = temp ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); // restore common factors of 2 return a < < k ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { int a = 34 b = 17 ; System . out . println ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari
Python # Iterative Python 3 program to # implement Stein's Algorithm # Function to implement # Stein's Algorithm def gcd ( a b ): # GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a # GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ): return b if ( b == 0 ): return a # Finding K where K is the # greatest power of 2 that # divides both a and b. k = 0 while ((( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ): a = a >> 1 b = b >> 1 k = k + 1 # Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ): a = a >> 1 # From here on 'a' is always odd. while ( b != 0 ): # If b is even remove all # factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ): b = b >> 1 # Now a and b are both odd. Swap if # necessary so a <= b then set # b = b - a (which is even). if ( a > b ): # Swap u and v. temp = a a = b b = temp b = ( b - a ) # restore common factors of 2 return ( a < < k ) # Driver code a = 34 b = 17 print ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' gcd ( a b )) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C# // Iterative C# program to implement // Stein's Algorithm using System ; class GFG { // Function to implement Stein's // Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ) { // Swap u and v. int temp = a ; a = b ; b = temp ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code public static void Main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; Console . Write ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal
JavaScript < script > // Iterative JavaScript program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( a b ) { /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; /*Finding K where K is the greatest power of 2 that divides both a and b. */ let k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } /* Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd */ while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; /* From here on 'a' is always odd. */ do { /* If b is even remove all factor of 2 in b */ while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ){ let t = a ; a = b ; b = t ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code let a = 34 b = 17 ; document . write ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); // This code contributed by gauravrajput1 < /script>
PHP // Iterative php program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( $a $b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( $a == 0 ) return $b ; if ( $b == 0 ) return $a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b. $k ; for ( $k = 0 ; (( $a | $b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ $k ) { $a >>= 1 ; $b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( $a & 1 ) == 0 ) $a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd. do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( $b & 1 ) == 0 ) $b >>= 1 ; // Now a and b are both odd. Swap // if necessary so a <= b then set // b = b - a (which is even) if ( $a > $b ) swap ( $a $b ); // Swap u and v. $b = ( $b - $a ); } while ( $b != 0 ); // restore common factors of 2 return $a < < $k ; } // Driver code $a = 34 ; $b = 17 ; echo 'Gcd of given numbers is ' . gcd ( $a $b ); // This code is contributed by ajit ?>
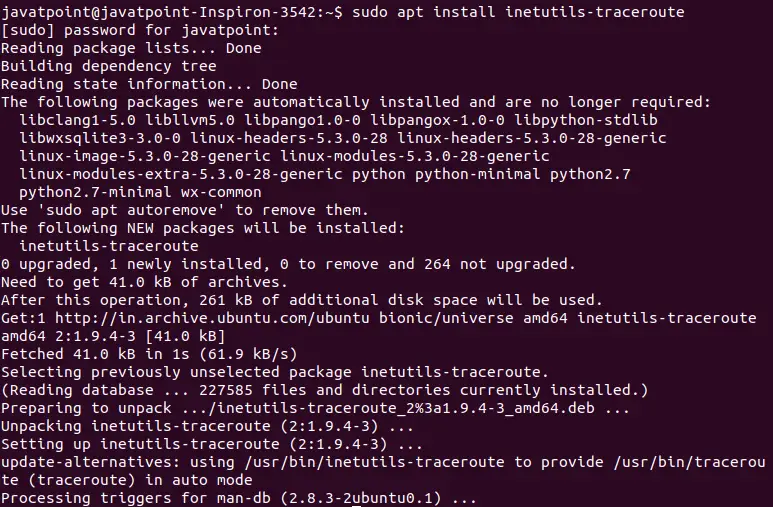
Výstup
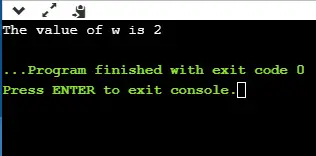
Gcd of given numbers is 17
Časová náročnost: O(N*N)
Pomocný prostor: O(1)
[Očekávaný přístup 2] Rekurzivní implementace - O(N*N) Čas a O(N*N) Plocha
C++ // Recursive C++ program to // implement Stein's Algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if ( ~ a & 1 ) // a is even { if ( b & 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } if ( ~ b & 1 ) // a is odd b is even return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code int main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; printf ( 'Gcd of given numbers is %d n ' gcd ( a b )); return 0 ; }
Java // Recursive Java program to // implement Stein's Algorithm import java.io.* ; class GFG { // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) // a is even { if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { int a = 34 b = 17 ; System . out . println ( 'Gcd of given' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari
Python # Recursive Python 3 program to # implement Stein's Algorithm # Function to implement # Stein's Algorithm def gcd ( a b ): if ( a == b ): return a # GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a # GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ): return b if ( b == 0 ): return a # look for factors of 2 # a is even if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ): # b is odd if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ): return gcd ( a >> 1 b ) else : # both a and b are even return ( gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ) # a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ): return gcd ( a b >> 1 ) # reduce larger number if ( a > b ): return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ) return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ) # Driver code a b = 34 17 print ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' gcd ( a b )) # This code is contributed # by Nikita Tiwari.
C# // Recursive C# program to // implement Stein's Algorithm using System ; class GFG { // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; // GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 // a is even if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) { // b is odd if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code public static void Main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; Console . Write ( 'Gcd of given' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( a b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) // a is even { if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver Code let a = 34 b = 17 ; document . write ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); < /script>
PHP // Recursive PHP program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( $a $b ) { if ( $a == $b ) return $a ; /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( $a == 0 ) return $b ; if ( $b == 0 ) return $a ; // look for factors of 2 if ( ~ $a & 1 ) // a is even { if ( $b & 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( $a >> 1 $b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( $a >> 1 $b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } if ( ~ $b & 1 ) // a is odd b is even return gcd ( $a $b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( $a > $b ) return gcd (( $a - $b ) >> 1 $b ); return gcd (( $b - $a ) >> 1 $a ); } // Driver code $a = 34 ; $b = 17 ; echo 'Gcd of given numbers is: ' gcd ( $a $b ); // This code is contributed by aj_36 ?>
Výstup
Gcd of given numbers is 17
Časová složitost : O(N*N) kde N je počet bitů ve větším čísle.
Pomocný prostor: O(N*N) kde N je počet bitů ve větším čísle.
Může se vám také líbit - Základní a rozšířený euklidovský algoritmus
Výhody oproti Euklidovu GCD algoritmu
- Steinův algoritmus je optimalizovaná verze Euklidova GCD algoritmu.
- je efektivnější při použití operátoru bitového posunu.