Třída Java.io.PipedOutputStream v Javě

Třída Java.io.PipedInputStream v Javě

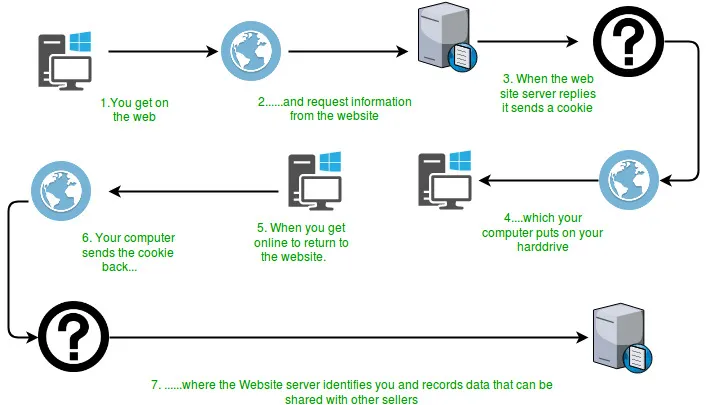
Trubky v IO poskytují spojení mezi dvěma vlákny běžícími v JVM současně. Potrubí se tedy používá jako zdroj nebo cíl.
- PipedInputStream je také přenášen pomocí PipedOutputStream. Data tedy mohou být zapsána pomocí PipedOutputStream a mohou být zapsána pomocí PipedInputStream. Ale použití obou vláken současně vytvoří pro vlákna uváznutí.
- PipedOutputStream odesílá konec kanálu. Data se zapisují do PipedOutputStream. Říká se, že roura je přerušená, pokud PipedInputStream, který četl data, již není.
Prohlášení:
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Konstruktor:
- PipedOutputStream() : vytvoří PipedOutputStream, který není připojen.
- PipedOutputStream(PipedOutputStream inStream) : vytvoří PipedOutputStream, že to
je připojen k PipedInputStream - 'inStream'.
Metody:
write() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(int byte) zapíše určený bajt do Piped Output Stream.
Syntaxe:
public void write(int byte)
Parameters :
byte : byte to be written
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) zapíše maxlen bajtů dat z vyrovnávací paměti do Piped Output Stream. Metoda se zablokuje, pokud do proudu nejsou zapsány žádné bajty.
Syntaxe:
public void write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : data of the buffer
offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'.
maxlen : maximum length of array to be read
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. Javavýstup:
Use of write(buffer offset maxlen) : J A V A
- close() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.close() zavře Piped Output Stream a uvolní přidělené zdroje.
Syntaxe:
public void close()
Parameters :
--------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- connect(cíl PipedInputStream) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.connect(cíl PipedInputStream připojuje zřetězený výstupní tok k 'cílovému' zřetězenému vstupnímu toku a v případě, že 'cíl' jsou roury s nějakým jiným tokem, je vyvolána IO výjimka
Syntaxe:
public void connect(PipedInputStream destination)
Parameters :
destination : the Piped Input Stream to be connected to
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- flush() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.flush() vyprázdní výstupní proud.
Syntaxe:
public void flush()
Parameters :
------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
Java kód ilustrující fungování metod třídy PipedOutputStream:
Javavýstup:
Use of flush() method :
G E E K S
Closing the Output stream
Vytvořit kvíz