Asymptotická analýza a porovnání třídicích algoritmů
Je dobře známou skutečností, že slučovací řazení probíhá rychleji než vkládání. Použití asymptotická analýza . můžeme dokázat, že slučovací řazení probíhá v čase O(nlogn) a řazení vkládání trvá O(n^2). Je to zřejmé, protože slučovací třídění používá přístup rozděl a panuj tím, že rekurzivně řeší problémy, kde při řazení vkládání následuje inkrementální přístup. Pokud ještě podrobněji prozkoumáme analýzu časové složitosti, zjistíme, že řazení vložení není tak špatné. Překvapivě vložení řazení beatů sloučení řazení na menší vstupní velikost. Je to proto, že existuje málo konstant, které při odvozování časové složitosti ignorujeme. U větších vstupních velikostí řádu 10^4 to neovlivňuje chování naší funkce. Ale když vstupní velikosti klesnou pod řekněme méně než 40, pak konstanty v rovnici dominují vstupní velikosti „n“. Zatím je vše dobré. Ale s takovou matematickou analýzou jsem nebyl spokojen. Jako student informatiky musíme věřit v psaní kódu. Napsal jsem program v jazyce C, abych získal představu o tom, jak proti sobě algoritmy soutěží o různé velikosti vstupu. A také proč se provádí tak přísná matematická analýza stanovení složitosti doby běhu těchto třídicích algoritmů.
Implementace:
CPP #include #include #include #include #define MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY 1000000001 int cmpfunc ( const void * a const void * b ) { // Compare function used by qsort return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } int * generate_random_array ( int n ) { srand ( time ( NULL )); int * a = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = rand () % MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ; return a ; } int * copy_array ( int a [] int n ) { int * arr = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) arr [ i ] = a [ i ]; return arr ; } // Code for Insertion Sort void insertion_sort_asc ( int a [] int start int end ) { int i ; for ( i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; ++ i ) { int key = a [ i ]; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; -- j ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Code for Merge Sort void merge ( int a [] int start int end int mid ) { int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; int * aux = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * ( end - start + 1 )); while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; else aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; } while ( i <= mid ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; while ( j <= end ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; j = 0 ; for ( i = start ; i <= end ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = aux [ j ++ ]; free ( aux ); } void _merge_sort ( int a [] int start int end ) { if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; _merge_sort ( a start mid ); _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void merge_sort ( int a [] int n ) { return _merge_sort ( a 0 n - 1 ); } void insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( int a [] int start int end int k ) { // Performs insertion sort if size of array is less than or equal to k // Otherwise uses mergesort if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { return insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ); } int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void test_sorting_runtimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Measuring the runtime of the sorting algorithms int number_of_times = num_of_times ; int t = number_of_times ; int n = size ; double insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 ; double merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 ; while ( t -- ) { clock_t start end ; int * a = generate_random_array ( n ); int * b = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 n - 1 ); end = clock (); insertion_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( b ); int * c = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); merge_sort ( c n ); end = clock (); merge_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( c ); int * d = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 n - 1 40 ); end = clock (); merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( d ); start = clock (); qsort ( a n sizeof ( int ) cmpfunc ); end = clock (); qsort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( a ); } insertion_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= number_of_times ; qsort_time /= number_of_times ; printf ( ' n Time taken to sort: n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f nn ' '(i)Insertion sort: ' insertion_sort_time '(ii)Merge sort: ' merge_sort_time '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time '(iv)Qsort library function: ' qsort_time ); } int main ( int argc char const * argv []) { int t ; scanf ( '%d' & t ); while ( t -- ) { int size num_of_times ; scanf ( '%d %d' & size & num_of_times ); test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ); } return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Scanner ; import java.util.Arrays ; import java.util.Random ; public class SortingAlgorithms { // Maximum element in array static final int MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; public static void main ( String [] args ) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ); int t = scanner . nextInt (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < t ; i ++ ) { int size = scanner . nextInt (); int num_of_times = scanner . nextInt (); testSortingRuntimes ( size num_of_times ); } scanner . close (); } static int [] generateRandomArray ( int n ) { // Generate an array of n random integers. int [] arr = new int [ n ] ; Random random = new Random (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { arr [ i ] = random . nextInt ( MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ); } return arr ; } static void insertionSortAsc ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for ( int i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { int key = a [ i ] ; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] ; j -- ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } static void merge ( int [] a int start int end int mid ) { // Merge two sorted sublists of a. // The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. int [] aux = new int [ end - start + 1 ] ; int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ] ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } else { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } System . arraycopy ( aux 0 a start aux . length ); } static void mergeSort ( int [] a ) { // Perform an in-place merge sort on a. mergeSortHelper ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } static void mergeSortHelper ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Recursive merge sort function. if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; mergeSortHelper ( a start mid ); mergeSortHelper ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } static void insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( int [] a int start int end int k ) { /* Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. */ if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } static void testSortingRuntimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. double insertionSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; double qsortTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < num_of_times ; i ++ ) { int [] a = generateRandomArray ( size ); int [] b = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); long start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); long end = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; int [] c = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSort ( c ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; int [] d = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; int [] e = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); Arrays . sort ( e ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= num_of_times ; qsortTime /= num_of_times ; System . out . println ( 'nTime taken to sort:n' + '(i) Insertion sort: ' + insertionSortTime + 'n' + '(ii) Merge sort: ' + mergeSortTime + 'n' + '(iii) Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' + mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime + 'n' + '(iv) Qsort library function: ' + qsortTime + 'n' ); } }
Python3 import time import random import copy from typing import List # Maximum element in array MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 def generate_random_array ( n : int ) -> List [ int ]: #Generate a list of n random integers. return [ random . randint ( 0 MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ) for _ in range ( n )] def insertion_sort_asc ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for i in range ( start + 1 end + 1 ): key = a [ i ] j = i - 1 while j >= start and a [ j ] > key : a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] j -= 1 a [ j + 1 ] = key def merge ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int mid : int ) -> None : #Merge two sorted sublists of a. #The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. aux = [] i = start j = mid + 1 while i <= mid and j <= end : if a [ i ] <= a [ j ]: aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 else : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 while i <= mid : aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 while j <= end : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 a [ start : end + 1 ] = aux def _merge_sort ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Recursive merge sort function. if start < end : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 _merge_sort ( a start mid ) _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ) merge ( a start end mid ) def merge_sort ( a : List [ int ]) -> None : #Perform an in-place merge sort on a. _merge_sort ( a 0 len ( a ) - 1 ) def insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int k : int ) -> None : ''' Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. ''' if start < end : size = end - start + 1 if size <= k : insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ) else : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ) insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ) merge ( a start end mid ) def test_sorting_runtimes ( size : int num_of_times : int ) -> None : #Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 for _ in range ( num_of_times ): a = generate_random_array ( size ) b = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 len ( b ) - 1 ) end = time . time () insertion_sort_time += end - start c = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () merge_sort ( c ) end = time . time () merge_sort_time += end - start d = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 len ( d ) - 1 40 ) end = time . time () merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += end - start start = time . time () a . sort () end = time . time () qsort_time += end - start insertion_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= num_of_times qsort_time /= num_of_times print ( f ' n Time taken to sort: n ' f '(i)Insertion sort: { insertion_sort_time } n ' f '(ii)Merge sort: { merge_sort_time } n ' f '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: { merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time } n ' f '(iv)Qsort library function: { qsort_time } n ' ) def main () -> None : t = int ( input ()) for _ in range ( t ): size num_of_times = map ( int input () . split ()) test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript // Importing required modules const { performance } = require ( 'perf_hooks' ); // Maximum element in array const MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; // Function to generate a list of n random integers function generateRandomArray ( n ) { return Array . from ({ length : n } () => Math . floor ( Math . random () * MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY )); } // Function to perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end function insertionSortAsc ( a start end ) { for ( let i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { let key = a [ i ]; let j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; j -= 1 ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Function to merge two sorted sublists of a function merge ( a start end mid ) { let aux = []; let i = start ; let j = mid + 1 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } else { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { a [ i ] = aux [ i - start ]; } } // Recursive merge sort function function _mergeSort ( a start end ) { if ( start < end ) { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); _mergeSort ( a start mid ); _mergeSort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } // Function to perform an in-place merge sort on a function mergeSort ( a ) { _mergeSort ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } // Function to perform an in-place sort on a from start to end function insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start end k ) { if ( start < end ) { let size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } // Function to test the runtime of the sorting algorithms function testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ) { let insertionSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; let qsortTime = 0 ; for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < numOfTimes ; _ ++ ) { let a = generateRandomArray ( size ); let b = [... a ]; let start = performance . now (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); let end = performance . now (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; let c = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); mergeSort ( c ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; let d = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; start = performance . now (); a . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); end = performance . now (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= numOfTimes ; qsortTime /= numOfTimes ; console . log ( `nTime taken to sort:n(i)Insertion sort: ${ insertionSortTime } n(ii)Merge sort: ${ mergeSortTime } n(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ${ mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime } n(iv)Qsort library function: ${ qsortTime } n` ); } // Main function function main () { let t = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of test cases: ' )); for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < t ; _ ++ ) { let size = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the size of the array: ' )); let numOfTimes = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of times to run the test: ' )); testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ); } } // Call the main function main ();
Porovnal jsem doby běhu následujících algoritmů:
- Řazení vložení : Tradiční algoritmus bez úprav/optimalizace. Funguje velmi dobře pro menší vstupní velikosti. A ano, porazí slučovací řazení
- Jde osud : Dodržuje přístup rozděl a panuj. Pro vstupní velikosti řádu 10^5 je tento algoritmus správnou volbou. Způsobuje to nepraktické řazení vložení pro tak velké vstupní velikosti.
- Kombinovaná verze řazení vložení a řazení: Trochu jsem vylepšil logiku řazení sloučení, abych dosáhl podstatně lepšího provozního času pro menší vstupní velikosti. Jak víme, merge sort rozděluje svůj vstup na dvě poloviny, dokud není dostatečně triviální pro třídění prvků. Ale když velikost vstupu klesne pod práh, jako je „n“ < 40 then this hybrid algorithm makes a call to traditional insertion sort procedure. From the fact that insertion sort runs faster on smaller inputs and merge sort runs faster on larger inputs this algorithm makes best use both the worlds.
- Rychlé řazení: Tento postup jsem nerealizoval. Toto je knihovní funkce qsort(), která je dostupná v . Zvažoval jsem tento algoritmus, abych poznal význam implementace. Minimalizuje počet kroků a maximálně využívá základní jazyková primitiva k co nejlepší implementaci algoritmu vyžaduje velkou odbornost v programování. To je hlavní důvod, proč se doporučuje používat funkce knihovny. Jsou napsány tak, aby zvládly cokoli a všechno. Optimalizují v maximální možné míře. A než zapomenu na svou analýzu, qsort() běží neuvěřitelně rychle na prakticky libovolné velikosti vstupu!
Analýza:
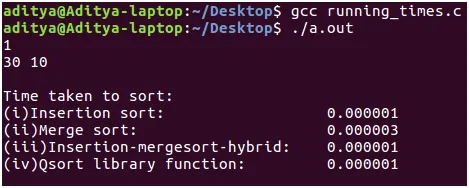
- Vstup: Uživatel musí zadat, kolikrát chce testovat algoritmus odpovídající počtu testovacích případů. Pro každý testovací případ musí uživatel zadat dvě celá čísla oddělená mezerou označující vstupní velikost ‚n‘ a ‚num_of_times‘ označující, kolikrát chce provést analýzu a udělat průměr. (Upřesnění: Je-li ‘num_of_times’ 10, pak se každý z výše uvedených algoritmů spustí 10krát a vezme se průměr. To se děje proto, že vstupní pole je generováno náhodně odpovídající zadané vstupní velikosti. Vstupní pole by mohlo být celé seřazeno. Mohlo by to odpovídat nejhoršímu případu .t. bere se průměr.) clock() rutina a makro CLOCKS_PER_SEC from se používá k měření času. Kompilace: Výše uvedený kód jsem napsal v prostředí Linuxu (Ubuntu 16.04 LTS). Zkopírujte výše uvedený fragment kódu. Zkompilujte jej pomocí klíče gcc ve vstupech, jak je uvedeno, a obdivujte sílu třídicích algoritmů!
- Výsledky: Jak můžete vidět u malých vstupních velikostí vložení řazení beatů sloučení řazení podle 2 * 10^-6 sec. Tento časový rozdíl ale není tak výrazný. Na druhou stranu hybridní algoritmus a funkce knihovny qsort() fungují stejně dobře jako řazení vložení.
 Vstupní velikost se nyní zvýší přibližně 100krát na n = 1000 z n = 30. Rozdíl je nyní hmatatelný. Sloučit řazení probíhá 10krát rychleji než vkládání. Mezi výkonem hybridního algoritmu a rutiny qsort() je opět souvislost. To naznačuje, že qsort() je implementován způsobem, který je víceméně podobný našemu hybridnímu algoritmu, tj. přepínání mezi různými algoritmy, aby se z nich dalo co nejlépe.
Vstupní velikost se nyní zvýší přibližně 100krát na n = 1000 z n = 30. Rozdíl je nyní hmatatelný. Sloučit řazení probíhá 10krát rychleji než vkládání. Mezi výkonem hybridního algoritmu a rutiny qsort() je opět souvislost. To naznačuje, že qsort() je implementován způsobem, který je víceméně podobný našemu hybridnímu algoritmu, tj. přepínání mezi různými algoritmy, aby se z nich dalo co nejlépe.  Nakonec se vstupní velikost zvýší na 10^5 (1 Lakh!), což je s největší pravděpodobností ideální velikost používaná v praktických scénářích. Ve srovnání s předchozím zadáním n = 1000, kde sloučení řazení beat vkládání řazení 10krát rychleji, je zde rozdíl ještě výraznější. Sloučit řazení bije vložení řazení 100krát! Hybridní algoritmus, který jsme napsali, ve skutečnosti provádí tradiční řazení sloučením tím, že běží o 0,01 sekundy rychleji. A konečně funkce knihovny qsort() nám konečně dokazuje, že implementace také hraje klíčovou roli při pečlivém měření provozních časů tím, že běží o 3 milisekundy rychleji! :D
Nakonec se vstupní velikost zvýší na 10^5 (1 Lakh!), což je s největší pravděpodobností ideální velikost používaná v praktických scénářích. Ve srovnání s předchozím zadáním n = 1000, kde sloučení řazení beat vkládání řazení 10krát rychleji, je zde rozdíl ještě výraznější. Sloučit řazení bije vložení řazení 100krát! Hybridní algoritmus, který jsme napsali, ve skutečnosti provádí tradiční řazení sloučením tím, že běží o 0,01 sekundy rychleji. A konečně funkce knihovny qsort() nám konečně dokazuje, že implementace také hraje klíčovou roli při pečlivém měření provozních časů tím, že běží o 3 milisekundy rychleji! :D

Poznámka: Nespouštějte výše uvedený program s n >= 10^6, protože to bude vyžadovat hodně výpočetního výkonu. Děkujeme a přejeme hodně štěstí při kódování! :)
Vytvořit kvíz