تسوية قائمة مرتبطة متعددة المستويات (العمق الحكيم)
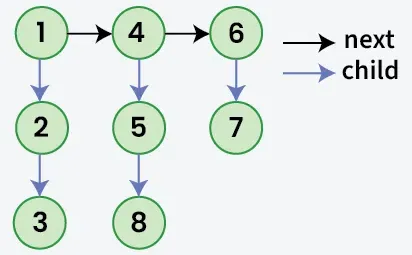
نظرا لقائمة مرتبطة حيث بالإضافة إلى التالي مؤشر كل عقدة لديه طفل المؤشر الذي قد يشير أو لا يشير إلى قائمة منفصلة. قد تحتوي قوائم الأطفال هذه على واحد أو أكثر أطفال خاصة بهم لإنتاج أ متعدد المستويات قائمة مرتبطة. نظرا إلى رأس التابع المستوى الأول من القائمة. المهمة هي تتسطح القائمة بحيث تظهر جميع العقد في ملف مستوى واحد قائمة مرتبطة. قم بتسوية القائمة بطريقة تجعل كافة العقد الموجودة في المستوى الأول يجب أن يأتي أولاً ثم العقد من ثانية المستوى وما إلى ذلك.
أمثلة:
مدخل:

الإخراج: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
توضيح: تم تسطيح القائمة المرتبطة متعددة المستويات لأنها لا تحتوي على مؤشرات فرعية.
لقد ناقشنا تسطيح قائمة مرتبطة متعددة المستويات حيث تحتوي العقد على مؤشرين للأسفل والتالي. في المنشور السابق نحن بالارض القائمة المرتبطة المستوى الحكيم. كيفية تسوية القائمة المرتبطة عندما نحتاج دائمًا إلى معالجة المؤشر لأسفل قبل التالي في كل عقدة.
جدول المحتويات
- [النهج المتوقع] استخدام العودية - O(n) الوقت وO(n) الفضاء
- [نهج بديل] استخدام المكدس - O(n) الوقت وO(n) الفضاء
[النهج المتوقع] استخدام العودية - O(n) الوقت وO(n) الفضاء
C++النهج هو بشكل متكرر تتسطح أ متعددة المستويات مرتبطة القائمة عن طريق اجتياز كل عقدة والعقد التابعة لها. أولاً تسوية قائمة الأطفال باستخدام العودية. بمجرد تسوية القائمة الفرعية، انتقل إلى العقدة التالية في التسلسل. أثناء الاجتياز، حافظ على أ مرجع إلى العقدة التي تمت زيارتها مسبقًا وربطه بالعقدة الحالية. تضمن هذه العملية ربط كافة العقد من مختلف المستويات في ملف واحد قائمة خطية واحدة مع الحفاظ على ترتيب عميق.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * curr Node *& prev ) { if ( curr == nullptr ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node * next = curr -> next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr -> down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); Node * prev = nullptr ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node curr Node [] prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] != null ) prev [ 0 ] . next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node [] prev = new Node [ 1 ] ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( curr prev ): if curr is None : return # Add the current element to the list. if prev [ 0 ] is not None : prev [ 0 ] . next = curr prev [ 0 ] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr . next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list ( curr . down prev ) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list ( next_node prev ) def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr is not None : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) prev = [ None ] flatten_list ( head prev ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node curr ref Node prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList ( curr . down ref prev ); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList ( next ref prev ); } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node prev = null ; FlattenList ( head ref prev ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( curr prev ) { if ( curr === null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] !== null ) prev [ 0 ]. next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer let next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); let prev = [ null ]; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head );
الإخراج
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[نهج بديل] استخدام المكدس - O(n) الوقت وO(n) الفضاء
C++النهج هو اجتياز قائمة مرتبطة متعددة المستويات باستخدام أ كومة . ابدأ دفع ال عقدة الرأس على المكدس. ثم بينما المكدس ليس فارغا البوب العقدة العلوية ومعالجتها. لكل عقدة يدفع إنه المؤشرات التالية والأسفل (إذا كانت موجودة) على المكدس. خلال هذه العملية ربط العقدة الحالية بالعقدة السابقة الحفاظ على القائمة في شكل مسطح. يضمن الاجتياز أن العقد من جميع المستويات متصلة في ملف قائمة مرتبطة ذات مستوى واحد الحفاظ على النظام الحكيم.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * head ) { if ( head == nullptr ) return ; stack < Node *> st ; st . push ( head ); Node * prev = nullptr ; while ( ! st . empty ()) { Node * curr = st . top (); st . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr -> next != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr -> down != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack ; class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack <> (); stack . push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( ! stack . isEmpty ()) { Node curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( head ): if head is None : return stack = [ head ] prev = None while stack : curr = stack . pop () # Push the next node first if curr . next : stack . append ( curr . next ) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr . down : stack . append ( curr . down ) # Add the current element to the list if prev : prev . next = curr prev = curr def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) flatten_list ( head ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack < Node > (); stack . Push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( stack . Count > 0 ) { Node curr = stack . Pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . Push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . Push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); FlattenList ( head ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( head ) { if ( head === null ) return ; let stack = [ head ]; let prev = null ; while ( stack . length > 0 ) { let curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next !== null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down !== null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev !== null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head );
الإخراج
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28