نظرية اللعبة التوافقية | المجموعة 4 (سبراغ - نظرية جراندي)
المتطلبات الأساسية : أرقام جراندي/أرقام وميكس
لقد رأينا بالفعل في المجموعة 2 (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/combinatorial-game-theory-set-2-game-nim/) أنه يمكننا العثور على من يفوز في لعبة Nim دون أن يلعب اللعبة فعليًا.
لنفترض أننا قمنا بتغيير لعبة Nim الكلاسيكية قليلاً. هذه المرة يمكن لكل لاعب إزالة 1 أو 2 أو 3 أحجار فقط (وليس أي عدد من الحجارة كما في لعبة Nim الكلاسيكية). هل يمكننا توقع من سيفوز؟
نعم يمكننا التنبؤ بالفائز باستخدام نظرية سبراغ-جروندي.
ما هي نظرية سبراغ-جروندي؟
لنفترض أن هناك لعبة مركبة (أكثر من لعبة فرعية واحدة) مكونة من ألعاب فرعية N ولاعبين A وB. ثم تقول نظرية Sprague-Grundy أنه إذا لعب كل من A وB على النحو الأمثل (أي لم يرتكبوا أي أخطاء) فإن اللاعب الذي يبدأ أولاً يضمن الفوز إذا كان XOR للأرقام الكبرى للمراكز في كل ألعاب فرعية في بداية اللعبة غير صفر. وإلا إذا تم تقييم XOR إلى الصفر، فسيخسر اللاعب A بالتأكيد مهما حدث.
كيفية تطبيق نظرية سبراغ جراندي؟
يمكننا تطبيق نظرية سبراغ-جروندي في أي شيء لعبة محايدة وحلها. يتم سرد الخطوات الأساسية على النحو التالي:
- تقسيم اللعبة المركبة إلى ألعاب فرعية.
- ثم لكل لعبة فرعية قم بحساب رقم Grundy في هذا الموضع.
- ثم قم بحساب XOR لجميع أرقام Grundy المحسوبة.
- إذا كانت قيمة XOR غير صفر، فإن اللاعب الذي سيقوم بالدور (اللاعب الأول) سيفوز وإلا فإنه مقدر له أن يخسر مهما حدث.
لعبة المثال: تبدأ اللعبة بـ 3 أكوام تحتوي على 3 و 4 و 5 أحجار ويمكن للاعب الذي ينقلها أن يأخذ أي عدد موجب من الحجارة حتى 3 فقط من أي أكوام [شريطة أن تحتوي الكومة على هذا القدر من الحجارة]. آخر لاعب يتحرك يفوز. من هو اللاعب الذي سيفوز باللعبة بافتراض أن كلا اللاعبين يلعبان على النحو الأمثل؟
كيف تعرف من سيفوز بتطبيق نظرية سبراغ-جروندي؟
كما نرى أن هذه اللعبة بحد ذاتها مكونة من عدة ألعاب فرعية.
الخطوة الأولى : يمكن اعتبار الألعاب الفرعية بمثابة كل أكوام.
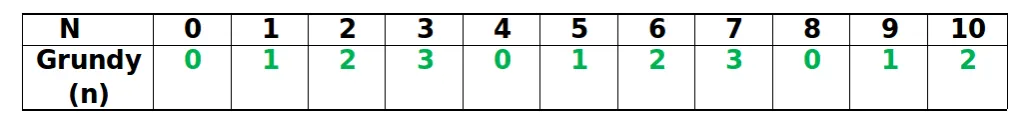
الخطوة الثانية : نرى من الجدول أدناه أن
Grundy(3) = 3 Grundy(4) = 0 Grundy(5) = 1

لقد رأينا بالفعل كيفية حساب أرقام Grundy لهذه اللعبة في سابق شرط.
الخطوة الثالثة : XOR لـ 3 0 1 = 2
الخطوة الرابعة : بما أن XOR رقم غير الصفر، فيمكننا القول أن اللاعب الأول هو الذي سيفوز.
وفيما يلي البرنامج الذي ينفذ الخطوات الأربع المذكورة أعلاه.
C++ /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ #include using namespace std ; /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ #define PLAYER1 1 #define PLAYER2 2 // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set int calculateMex ( unordered_set < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . find ( Mex ) != Set . end ()) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy []) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != -1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); unordered_set < int > Set ; // A Hash Table for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . insert ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); } return ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main () { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = sizeof ( piles ) / sizeof ( piles [ 0 ]); // Find the maximum element int maximum = * max_element ( piles piles + n ); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [ maximum + 1 ]; memset ( Grundy -1 sizeof ( Grundy )); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ return ( 0 ); }
Java import java.util.* ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; static int PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < Integer > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy [] ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ] ); // A Hash Table HashSet < Integer > Set = new HashSet < Integer > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ] ); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]] ; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]] ; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = Arrays . stream ( piles ). max (). getAsInt (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [] = new int [ maximum + 1 ] ; Arrays . fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3 ''' Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing''' PLAYER1 = 1 PLAYER2 = 2 # A Function to calculate Mex of all # the values in that set def calculateMex ( Set ): Mex = 0 ; while ( Mex in Set ): Mex += 1 return ( Mex ) # A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' def calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ): Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ): return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A Hash Table Set = set () for i in range ( 1 4 ): Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )) # Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ) return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A function to declare the winner of the game def declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ): xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for i in range ( 1 n ): xorValue = ( xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]) if ( xorValue != 0 ): if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : # Test Case 1 piles = [ 3 4 5 ] n = len ( piles ) # Find the maximum element maximum = max ( piles ) # An array to cache the sub-problems so that # re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided Grundy = [ - 1 for i in range ( maximum + 1 )]; # Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for i in range ( n ): calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); ''' Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); ''' # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; using System.Collections.Generic ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; //static int PLAYER2 = 2; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . Contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int [] Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table HashSet < int > Set = new HashSet < int > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . Add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int [] piles int [] Grundy int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code static void Main () { // Test Case 1 int [] piles = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . Length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = piles . Max (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int [] Grundy = new int [ maximum + 1 ]; Array . Fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by mits
JavaScript < script > /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ let PLAYER1 = 1 ; let PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set function calculateMex ( Set ) { let Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . has ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' function calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table let Set = new Set (); for ( let i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game function declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ) { let xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); } return ; } // Driver code // Test Case 1 let piles = [ 3 4 5 ]; let n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element let maximum = Math . max (... piles ) // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided let Grundy = new Array ( maximum + 1 ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maximum + 1 ; i ++ ) Grundy [ i ] = 0 ; // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( let i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 < /script>
الإخراج :
Player 1 will win
التعقيد الزمني : O(n^2) حيث n هو الحد الأقصى لعدد الحجارة في الكومة.
تعقيد الفضاء: O(n) حيث يتم استخدام مصفوفة Grundy لتخزين نتائج المشكلات الفرعية لتجنب الحسابات الزائدة عن الحاجة وتستغرق مساحة O(n).
مراجع :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sprague%E2%80%93Grundy_theorem
تمرين للقراء: النظر في اللعبة أدناه.
يتم لعب لعبة بين لاعبين بعدد N الصحيح A1 A2 .. AN. في دوره، يختار اللاعب عددًا صحيحًا ويقسمه على 2 3 أو 6 ثم يأخذ الكلمة. إذا أصبح العدد الصحيح 0 تتم إزالته. آخر لاعب يتحرك يفوز. من هو اللاعب الذي يفوز باللعبة إذا لعب كلا اللاعبين على النحو الأمثل؟
تلميح: انظر المثال 3 من سابق شرط.